Themed collection Nanoscale Biomaterials

Themed issue on nanoscale biomaterials
Guest editors Jordan J. Green and Jason A. Burdick introduce this Journal of Materials Chemistry B themed issue on nanoscale biomaterials.
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8039-8042
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB90123A
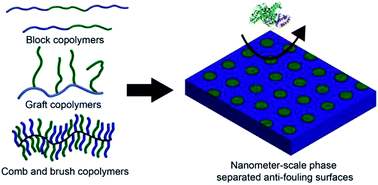
Nanometer-scale self-assembly of amphiphilic copolymers to control and prevent biofouling
A review of amphiphilic copolymers that phase separate on the nanometer-scale to create coatings that prevent biofouling.
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8043-8052
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00961D
Biomaterials at the interface of nano- and micro-scale vector–cellular interactions in genetic vaccine design
The development of safe and effective vaccines for the prevention of elusive infectious diseases remains a public health priority.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8053-8068
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB01058B
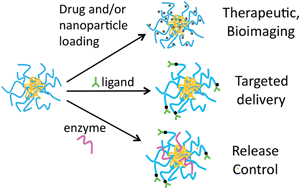
Nanogel carrier design for targeted drug delivery
Polymer-based nanogel formulations offer features attractive for drug delivery, including ease of synthesis, controllable swelling and viscoelasticity as well as drug loading and release characteristics, passive and active targeting, and the ability to formulate nanogel carriers that can respond to biological stimuli.
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8085-8097
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB01141D
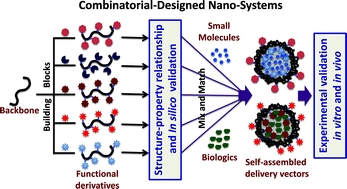
Combinatorial approach in the design of multifunctional polymeric nano-delivery systems for cancer therapy
This update summarizes the recent advances in combinatorial design of polymeric material for developing multifunctional nanovectors to deliver nucleic acids and chemodrugs for cancer therapy.
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8069-8084
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB01083C
Nanocoating for biomolecule delivery using layer-by-layer self-assembly
Schematic illustrates the formation of LbL coatings using different methods. (A) Electrostatic interactions; (B) Hydrogen bonding; or (C) Biological interactions.
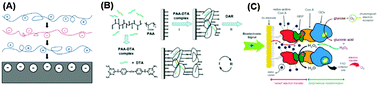
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2015,3, 8757-8770
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00450K
Improved cell infiltration of highly porous 3D nanofibrous scaffolds formed by combined fiber–fiber charge repulsions and ultra-sonication
Hydrogel mats with increased thickness and porosity were achieved by pairing high humidity electrospinning with post-processing ultra-sonication, and they show promise for the design of cell-permeable nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue-engineering applications.
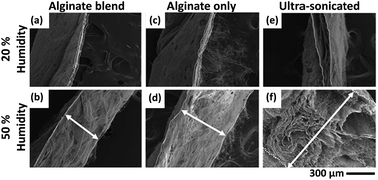
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8116-8122
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB01487A
Enhanced non-viral gene delivery to human embryonic stem cells via small molecule-mediated transient alteration of the cell structure
Y-27632 enhances the transfection efficiencies of various polyplexes or lipoplexes in hESCs via increased membrane exposure through transient spreading of the cells.
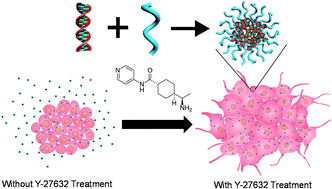
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8098-8105
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00750F
Shape transformation following reduction-sensitive PEG cleavage of polymer/DNA nanoparticles
lPEI-g-PEG/DNA nanoparticles transform their shape from worm-like to condensed spheres and short rods following cleavage of PEG chains.
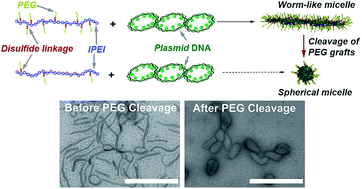
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8106-8109
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00967C
Ordered, adherent layers of nanofibers enabled by supramolecular interactions
Aligned nanofibrous substrates were organized into multilamellar structures using macroscopic assembly through guest–host interactions of modified fibers and polymer chains.
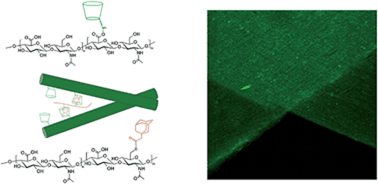
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8110-8115
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00724G
A CMP-based method for tunable, cell-mediated gene delivery from collagen scaffolds
Collagen mimetic peptides (CMP)s were used to tailor release vs. retention of DNA polyplexes from collagen while preserving polyplex activity.
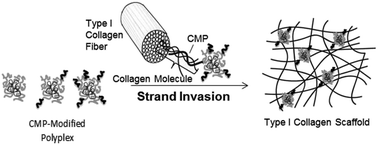
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8174-8185
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB01435A
Theranostic nanoscale coordination polymers for magnetic resonance imaging and bisphosphonate delivery
Mn-zoledronate NCP carries 63 wt% of zoledronate for cancer therapy and 13 wt% of Mn2+ for T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8249-8255
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00751D
Dextran coated bismuth–iron oxide nanohybrid contrast agents for computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging
A novel synthesis of dextran coated bismuth–iron oxide nanoparticles (BION) is reported. They are found to be effective as contrast agents for both CT and MRI and to be both biodegradable and biocompatible.
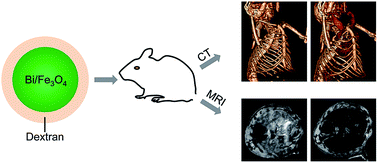
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8239-8248
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB01159G
Covalent layer-by-layer assembly of hyperbranched polymers on alginate microcapsules to impart stability and permselectivity
Hyperbranched functionalized polymers, coated onto capsules in a covalent layer-by-layer manner, provide a facile platform for modulation of hydrogel permselectivity and stability.
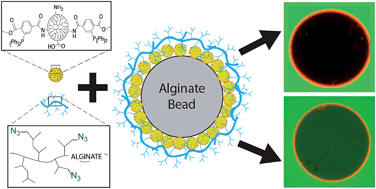
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8208-8219
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB01241K
A dual gold nanoparticle system for mesenchymal stem cell tracking
A gold nanoparticle system was developed which is capable of monitoring both delivered stem cells and infiltrating macrophages in vivo using photoacoustic imaging.
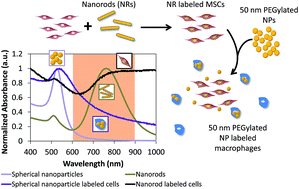
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8220-8230
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00975D
Structural elucidation of cell membrane-derived nanoparticles using molecular probes
Engineering cell membranes with molecular probes enables studying the orientation and permeability of cell membrane-derived nanoparticles.
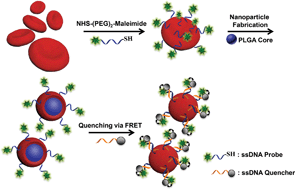
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8231-8238
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00980K
Inhibition of atherosclerosis-promoting microRNAs via targeted polyelectrolyte complex micelles
Polyelectrolyte complex micelles have great potential as gene delivery vehicles because of their ability to encapsulate charged nucleic acids forming a core by neutralizing their charge, while simultaneously protecting the nucleic acids from non-specific interactions and enzymatic degradation.
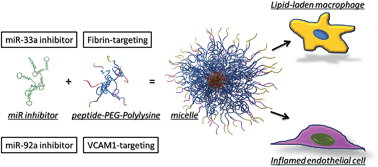
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8142-8153
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00977K
Phospholipase A2-responsive antibiotic delivery via nanoparticle-stabilized liposomes for the treatment of bacterial infection
A unique nanoparticle delivery system is reported for on-demand antibiotic release to locally and effectively treat bacterial infection.
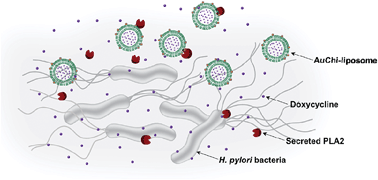
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8201-8207
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB01110D
Sustained release of bupivacaine for post-surgical pain relief using core–shell microspheres
Core–shell PLGA/PLLA polymer microspheres sustained 2 weeks in vivo bupivacaine release, providing extended postoperative analgesia without infection or joint damage.
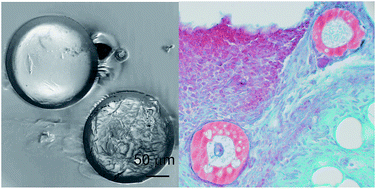
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8194-8200
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00948G
3-D scaffold platform for optimized non-viral transfection of multipotent stem cells
An enhanced throughput, 3D scaffold platform can be used to screen for the influence of mineral coating properties on stem cell transfection.
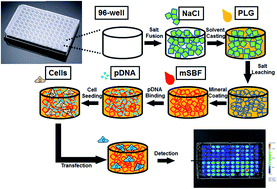
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8186-8193
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00957F
Lacritin-mediated regeneration of the corneal epithelia by protein polymer nanoparticles
Protein polymer nanoparticles decorated with the mitogenic human tear protein, lacritin, heal a defect in the corneal epithelium faster than a soluble control peptide.
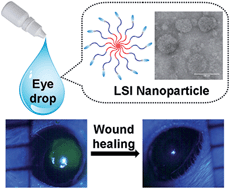
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8131-8141
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00979G
Multi-responsive hydrogels derived from the self-assembly of tethered allyl-functionalized racemic oligopeptides
A multi-responsive oligopeptide-based hydrogel system with synthetic feasibility and potential for functionalization provided a platform for intelligent bio-functional and bio-responsive materials.
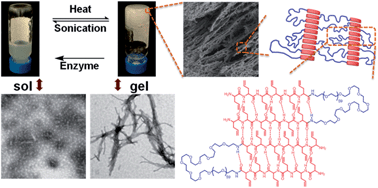
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8123-8130
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00909F
Enhanced performance of plasmid DNA polyplexes stabilized by a combination of core hydrophobicity and surface PEGylation
Nonviral gene therapy has high potential for safely promoting tissue restoration and for treating various genetic diseases.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8154-8164
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00352G
Highly compacted pH-responsive DNA nanoparticles mediate transgene silencing in experimental glioma
Complex genetic mutations are common in brain cancer, making gene therapy an attractive approach to repair or modulate altered genes and cellular pathways.
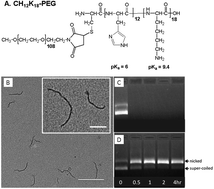
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014,2, 8165-8173
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00559G
About this collection
The development of new biomaterials is an area of research that is rapidly advancing, nanoscale biomaterials comprise materials designed to interact at the molecular level with biological systems. This size scale has important implications for interactions with cells and tissues, from single interactions of cellular receptors with extracellular matrix molecules to the control of cell trafficking throughout the body. With this size scale in mind, nanoscale biomaterials are being developed for a range of applications from drug delivery to tissue engineering. This special issue focuses on diverse materials ranging from nanoparticles/nanogels to nanofibers and nanoscale coatings to molecular probes for imaging.