Themed collection 2017 Perspective articles collection

Ultraviolet radiation-induced immunosuppression and its relevance for skin carcinogenesis
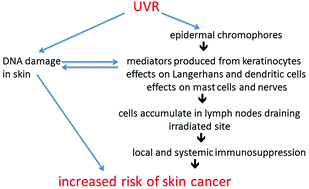
Major steps in the pathway leading to the increased risk of skin cancer by the immunosuppression induced by UVR exposure.
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2018,17, 1872-1884
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7PP00312A
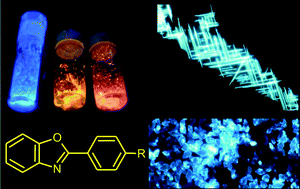
2-Phenylbenzoxazole derivatives: a family of robust emitters of solid-state fluorescence
In addition to thermal, chemical and photochemical stability, the 2-phenylbenzoxazole fragment exhibits attractive emission properties in the solid state, thus leading to highly photoluminescent materials and sensors.
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 1020-1035
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7PP00112F
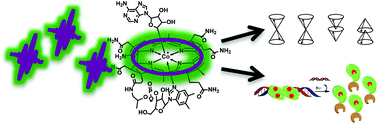
The photochemistry and photobiology of vitamin B12
This Perspective provides the first detailed overview of the photoresponse of vitamin B12 and its derivatives, from the early, photophysical events to the burgeoning area of B12-dependent photobiology.
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 820-834
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7PP00054E
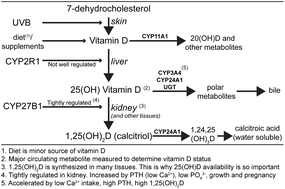
Sunlight exposure is just one of the factors which influence vitamin D status
Studies on the determinants of vitamin D status have tended to concentrate on input – exposure to ultraviolet B radiation and the limited sources in food.
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 302-313
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00329J
The role of UV radiation and vitamin D in the seasonality and outcomes of infectious disease
Individual components of solar radiation, UVA, UVB and heat generation, are linked to their downstream immune functions, inducing vitamin D production, demonstrating a great degree of overlap between various components.
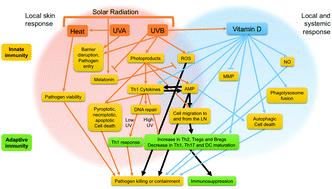
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 314-338
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00355A
Challenge and perspective: the relevance of ultraviolet (UV) radiation and the vitamin D endocrine system (VDES) for psoriasis and other inflammatory skin diseases
Focussing on the UV induced cutaneous synthesis of vitamin D, this review gives an update on the relevance of the VDES and of UV radiation for the management of psoriasis and other inflammatory skin diseases.
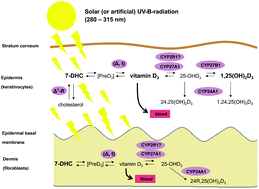
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 433-444
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00280C
ASTHMA – comparing the impact of vitamin D versus UVR on clinical and immune parameters
Asthma is estimated to affect more than 300 million individuals worldwide. Vitamin D is increasingly believed to beneficially influence asthma incidence and control, likely due to effects on innate and adaptive immunity. The primary mechanism for increasing vitamin D in the body is via UVB radiation of skin, however whether UVB has comparable effects to vitamin D on relevant immune mechanisms and asthma is unclear.
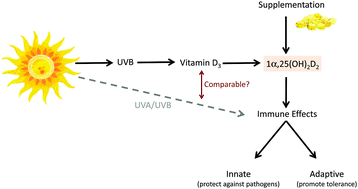
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 399-410
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00407E
The health benefits of UV radiation exposure through vitamin D production or non-vitamin D pathways. Blood pressure and cardiovascular disease
UV photoreduces nitrogen oxides sequestered in the skin. The resulting NO moves to the systemic circulation where it vasodilates and lowers BP.

Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 374-380
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00336B
Ultraviolet radiation, vitamin D and the development of obesity, metabolic syndrome and type-2 diabetes
Obesity prevalence is increasing around the world; however, the causes are not known. Here, we discuss moderate sun exposure as a potential modifier of obesity and metabolic dysfunction, with a focus on sun-induced mediators such as vitamin D and nitric oxide.
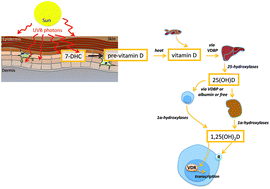
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 362-373
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00274A
The relationship between sun exposure and all-cause mortality
Women with low sun exposure are at a dose-dependently increased risk of all-cause mortality, mainly due to an increased risk of death from cardiovascular or noncancer/noncardiovascular disease compared higher exposure.
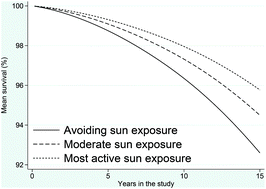
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 354-361
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00316H
Are low sun exposure and/or vitamin D risk factors for type 1 diabetes?
Ultraviolet radiation and vitamin D, with their known immunosuppressive effects, have the potential to delay or inhibit type 1 diabetes.
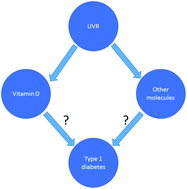
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 381-398
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00294C
A short history of phototherapy, vitamin D and skin disease
The earliest record between sun exposure and skin disease goes back five millennia to the ancient Egyptians. Cod liver oil was a folk remedy prior to 1789 and with the observation that sunlight prevented the “appearance of mycelial fungi” in 1877 the modern era commenced with the treatment of cutaneous Mycobacterium tuberculosis.

Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 283-290
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00406G
UVB radiation, vitamin D and multiple sclerosis
Acheson et al. (1960) observed an inverse relationship between sunlight exposure and the incidence of Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
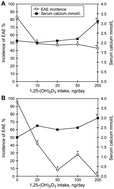
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 411-415
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00308G
Does sunlight protect us from cancer?
The Ultraviolet (UV) radiation contained in sunlight is a powerful mutagen and immune suppressant which partly explains why exposure to solar UV is the biggest risk factor for the development of cutaneous tumours.

Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 416-425
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00332J
Time outdoors, blood vitamin D status and myopia: a review
Myopia is a major public health concern throughout the world but whether vitamin D played a role in myopia development remains unknown.
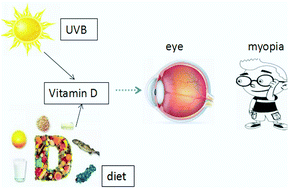
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 426-432
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00292G
Lung development
Recent equivocal results in high profile randomised controlled trials suggest that the impact of vitamin D deficiency on lung development is complex. In this narrative review we summarise our current understanding of the link between UV exposure, vitamin D and lung development.
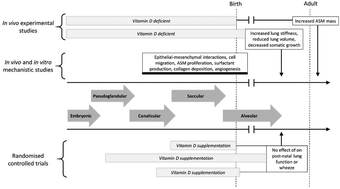
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 339-346
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00278A
UVR: sun, lamps, pigmentation and vitamin D
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UVR) has important and significant consequences on human health.
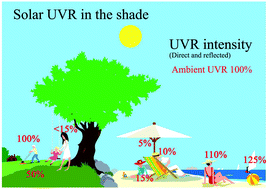
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 291-301
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00277C
The role of UVR and vitamin D on T cells and inflammatory bowel disease
Vitamin D/UVR effects on T cells that are important in the development of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
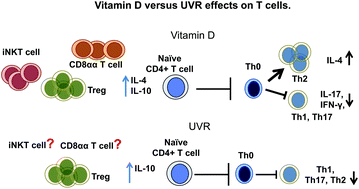
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 347-353
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PP00266H
Environmental effects of ozone depletion and its interactions with climate change: Progress report, 2016
After entering Earth's atmosphere, solar UV radiation is selectively attenuated by a variety of gaseous, particulate, and dissolved compounds. These include ozone and smoke in the atmosphere, and dissolved organic carbon in both inland waters and marine ecosystems.
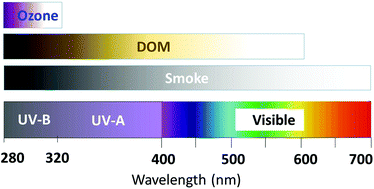
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017,16, 107-145
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7PP90001E
About this collection
This web collection contains Perspective articles that Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences has published in 2017.