Themed collection Computational and systems biology

Computational and Systems Biology
M. Madan Babu and Hirotada Mori introduce this themed issue of Molecular BioSystems focusing on Computational and systems biology

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1391-1391
https://doi.org/10.1039/B921381N
Logical modelling of cell cycle control in eukaryotes: a comparative study
The use of qualitative approaches for modelling the cell cycle is presented and discussed.
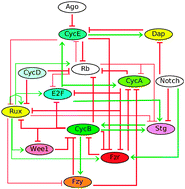
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1569-1581
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907562N
From genes to cells to tissues—modelling the haematopoietic system
Many important questions in the haematopoietic system remain unanswered or even unanswerable with current experimental tools. Scientists have therefore increasingly turned to modelling to tackle complexity at multiple levels ranging from networks of genes to the behaviour of cells and tissues.
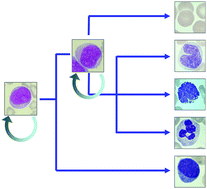
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1413-1420
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907225J
The powerful law of the power law and other myths in network biology
Topological properties such as the power law, small world and scale-freeness have been claimed as “universal laws” for biological and other complex networks. However these properties are contradicted by statistical or even by visual comparison of the observed distribution (green) with the power law (blue). We review and discuss the field of network biology and its relevance in terms of function and evolution.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1482-1493
https://doi.org/10.1039/B908681A
Supervised learning with decision tree-based methods in computational and systems biology
An accessible and comprehensive introduction to decision tree-based methods for supervised learning in computational and systems biology.
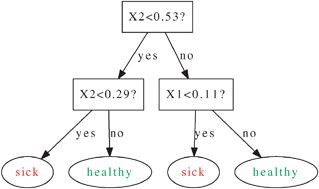
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1593-1605
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907946G
Systems analyses of circadian networks
We review the contribution that systems approaches have made to the understanding of the circadian clock in Arabidopsis thaliana and compare this to systems analyses of mammalian circadian clocks.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1502-1511
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907714F
Global signatures of protein and mRNA expression levels
Large-scale technology has enabled us to measure and compare protein and mRNA expression in different organisms. From these data we gain insights on the underlying regulation of translation and protein degradation.
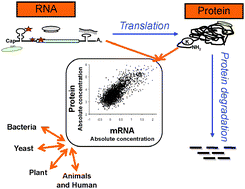
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1512-1526
https://doi.org/10.1039/B908315D
Nucleosome positioning—what do we really know?
This review addresses whether a genomic code for nucleosome positioning exists and how nucleosome arrays are organised in vivo.
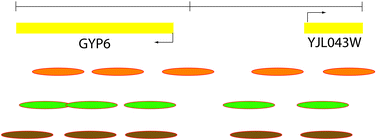
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1582-1592
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907227F
ChIPing away at the genome : the new frontier travel guide
Mapping protein–DNA interactions in vivo via chromatin immunoprecipitation and microarrays or sequencing provides powerful insights into genome organisation and transcriptional regulation.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1421-1428
https://doi.org/10.1039/B906179G
Structural interactomics: informatics approaches to aid the interpretation of genetic variation and the development of novel therapeutics
This review focuses on the use of structural interactomics in the development of novel therapeutics.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1456-1472
https://doi.org/10.1039/B906402H
Conformational averaging in structural biology: issues, challenges and computational solutions
The authors review different aspects of the problem of conformational averaging in structural biology experiments, discuss the pitfalls of the associated “single-structure paradigm” and describe different computational solutions to address the problem.
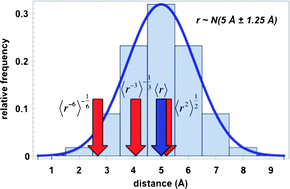
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1606-1616
https://doi.org/10.1039/B917186J
Explorations in topology–delving underneath the surface of genetic interaction maps
This review focuses on the methodologies currently available for using and interpreting large datasets of genetic interactions for functional gene groups, elaborates on the challenges ahead and highlights the need for comprehensive integrative analysis to extract the wealth of information found.
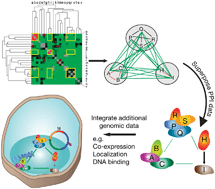
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1473-1481
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907076C
Modelling the Drosophila embryo
This historical overview on modelling pattern formation in the early Drosophila embryo shows how experimental and theoretical approaches have converged over the past decades to create a powerful new methodology for the systems-level study of developmental gene regulatory networks.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1549-1568
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904722K
Scoring overlapping and adjacent signals from genome -wide ChIP and DamID assays
We review existing quantitative methods to score overlaps, and to cluster binding events in ChIP and DamID profiles. We provide a simple guide to some of the statistical tools used by these methods.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1429-1438
https://doi.org/10.1039/B906880E
The potential of microfluidic water-in-oil droplets in experimental biology
Droplets with femto- to nanolitre volumes, handled in microfluidic devices, are an increasingly popular platform for high-throughput experiments that can be carried out under controlled conditions with a quantitative readout.
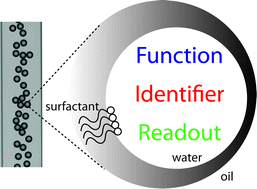
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1392-1404
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907578J
Signal initiation in biological systems: the properties and detection of transient extracellular protein interactions
Extracellular glycoprotein interactions are not detected by most high throughput assays creating “blind-spots” in protein interaction maps. This review examines this problem and discusses recent advances that have begun to address it.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1405-1412
https://doi.org/10.1039/B903580J
Theoretical models of spontaneous activity generation and propagation in the developing retina
In the developing retina, nearby neurons are spontaneously active, producing progagating patterns of activity, known as retinal waves. In this article we review several computational models used to help evaluate the mechanisms that might be responsible for the generation of retinal waves.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1527-1535
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907213F
Structure and organization of drug -target networks: insights from genomic approaches for drug discovery
Recent explosion in the amount of “omics” data opens new ways of predicting novel drugs and drug targets using network-based approaches.
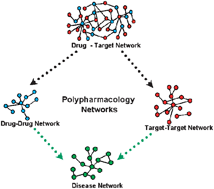
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1536-1548
https://doi.org/10.1039/B908147J
Scaling relationship in the gene content of transcriptional machinery in bacteria
The metabolic, defensive, communicative and pathogenic capabilities of eubacteria depend on their repertoire of genes and ability to regulate the expression of them. Sigma and transcription factors have fundamental roles in controlling these processes.
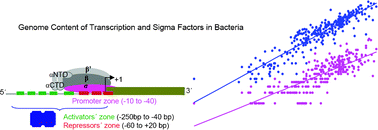
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1494-1501
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907384A
Systems-level approaches for identifying and analyzing genetic interaction networks in Escherichia coli and extensions to other prokaryotes
Escherichia coli may hold the key to understanding the unique biomolecular properties of prokaryotic cells. Recent advances in high-throughput screening techniques and subsequent results are discussed here.
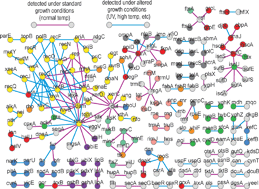
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1439-1455
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907407D
Correlation between mRNA expression levels and protein aggregation propensities in subcellular localisations
We investigate the relationship between mRNA expression levels and protein aggregation propensities at the proteomic level, and find that these quantities exhibit a significant correlation when they are averaged across subcellular localisations.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1873-1876
https://doi.org/10.1039/B913099N
The ABC of reverse engineering biological signalling systems
We discuss a statistical approach—approximate Bayesian computation (ABC)—which allows us to approximate the posterior distribution over model-parameters and show how this can add insights into our understanding of the system dynamics.
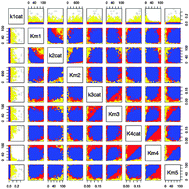
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1925-1935
https://doi.org/10.1039/B908951A
Energy based approach for understanding the recognition mechanism in protein –protein complexes
A novel energy based approach for identifying the binding site residues in protein–protein complexes showed the importance of cation–π, electrostatic and aromatic interactions with charged and aromatic residues at binding sites.
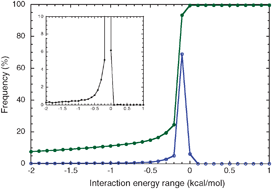
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1779-1786
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904161N
A c-Myc regulatory subnetwork from human transposable element sequences
We evaluated the contribution of transposable elements (TEs) to the c-Myc regulatory network by searching for c-Myc binding sites derived from TEs and by analyzing the expression and function of target genes with nearby TE-derived c-Myc binding sites.
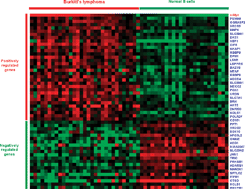
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1831-1839
https://doi.org/10.1039/B908494K
Ligand dependent intra and inter subunit communication in human tryptophanyl tRNA synthetase as deduced from the dynamics of structure networks
Homodimeric protein tryptophanyl tRNA synthetase (TrpRS) has a Rossmann fold domain and belongs to the 1c subclass of aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. In this study, we have modeled the structure of human TrpRS bound to the activated ligand and the cognate tRNA.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1860-1872
https://doi.org/10.1039/B903807H
Coding DNA repeated throughout intergenic regions of the Arabidopsis thaliana genome: evolutionary footprints of RNA silencing
Pyknons are non-random sequence patterns significantly repeated throughout non-coding genomic DNA. DNA sequence patterns from the Arabidopsis thaliana genome were detected using a probability-based method. We postulate that RNA-mediated gene silencing leads to the accumulation of gene sequences in non-coding DNA regions.
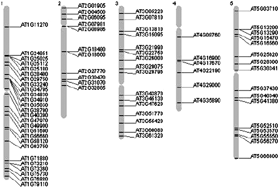
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1679-1687
https://doi.org/10.1039/B903031J
A metabolomic and multivariate statistical process to assess the effects of genotoxins in Saccharomycescerevisiae
A combined high resolution 1H NMR and gas chromatography mass spectrometry based metabolomic approach was used to monitor and distinguish different genotoxic compounds from other types of toxic lesion.
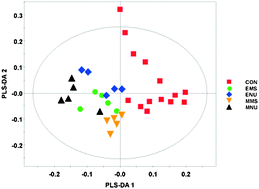
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1913-1924
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907754E
Relative stability of DNA as a generic criterion for promoter prediction: whole genome annotation of microbial genomes with varying nucleotide base composition
The relative lower stability of promoter regions as compared to neighboring genomic sequences has been used to develop an algorithm ‘PromPredict' for promoter identification. It is found to be very reliable when applied to whole genome annotation for microbial genome sequences.
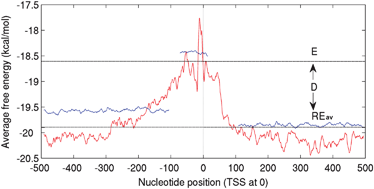
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1758-1769
https://doi.org/10.1039/B906535K
Signaling network analysis of ubiquitin-mediated proteins suggests correlations between the 26S proteasome and tumor progression
We performed a comprehensive analysis of a literature-mined human signaling network by integrating data on ubiquitin-mediated protein half-lives. Our findings have implications for the development of cancer treatments and prognostic markers focused on the ubiquitination machinery.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1809-1816
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905382D
Signal amplification in a lattice of coupled protein kinases
Bacteria such as Escherichia coli can detect remarkably low concentrations of nutrients such as amino acids. We explain this sensitivity by postulating an amplification step in the signal cascade due to cooperative interactions between molecules of the protein kinase CheA.
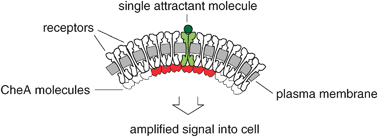
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1853-1859
https://doi.org/10.1039/B903397A
Molecular modeling and docking studies of human 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A (5-HT2A) receptor for the identification of hotspots for ligand binding
We have performed sequence analysis and molecular modeling of 5-HT2A that has revealed a set of conserved residues and motifs considered to play an important role in maintaining structural integrity and function of the receptor.
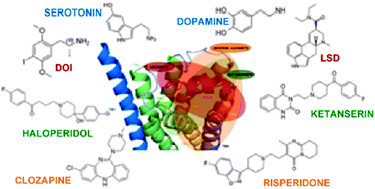
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1877-1888
https://doi.org/10.1039/B906391A
Predicting essential genes based on network and sequence analysis
Integrating the topological characteristics of protein–protein interaction networks and the gene sequence properties, we present a machine learning approach for the prediction of essential genes.
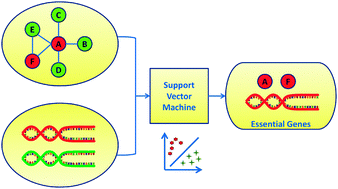
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1672-1678
https://doi.org/10.1039/B900611G
A network-based method for predicting gene –nutrient interactions and its application to yeast amino-acid metabolism
We present a new computational method for predicting metabolic gene–nutrient interactions (GNI) that uncovers the dependence of gene essentiality on the presence or absence of nutrients in the growth medium.
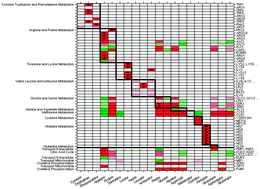
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1732-1739
https://doi.org/10.1039/B823287N
Unraveling the potential of intrinsically disordered proteins as drug targets: application to Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Tuberculosis remains a disease that causes havoc despite efforts to conquer the pathogen using structure-based rational drug design. We try to unravel thirteen intrinsically disordered essential proteins as potential drug targets with particular focus on GlmU, FtsW and Obg.
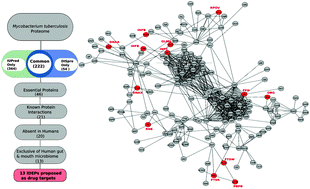
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1752-1757
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905518P
Dissection of USP catalytic domains reveals five common insertion points
This paper provides a detailed map of ubiquitin specific protease (USP) catalytic domains from human and yeast, revealing large insertions that intersperse the catalytic fold at five points.
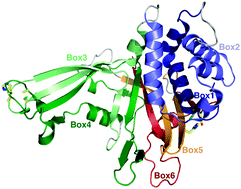
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1797-1808
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907669G
A global view of Escherichia coli Rsd protein and its interactions
The Escherichia coli Rsd protein forms 1 : 1 complexes with σ70 protein, which is the major factor in determining promoter recognition by RNA polymerase. Here we describe measurements of the levels of Rsd, RNA polymerase, σ70 and the alternative σ38 factor.
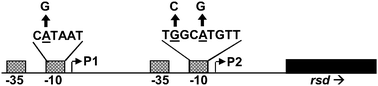
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1943-1947
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904955J
Modular logical modelling of the budding yeast cell cycle
This manuscript presents a logical compositional modelling method and its application to the budding yeast cell cycle. The resulting model couples three regulatory modules: the core cycling engine, the morphogenetic checkpoint and mitotic exit, and qualitatively accounts for the wild-type and numerous mutant behaviours.
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1787-1796
https://doi.org/10.1039/B910101M
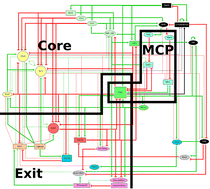
Prediction of conditional gene essentiality through graph theoretical analysis of genome -wide functional linkages
We demonstrate the efficacy of combined graph theoretical and machine learning approaches in ranking essential nodes from a large network of genome-wide functional linkages, which yields predictions with high accuracy. We therefore perceive such predictions as highly useful in applications such as defining and prioritizing drug targets.
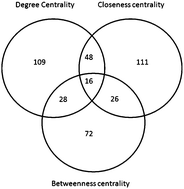
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1936-1942
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905264J
An integrative approach towards completing genome -scale metabolic networks
We propose a strategy that incorporates genomic sequence data and metabolite profiles into modelling approaches to arrive at improved gene annotations and more complete genome-scale metabolic networks.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1889-1903
https://doi.org/10.1039/B915913B
Transcription regulatory networks in Caenorhabditis elegans inferred through reverse-engineering of gene expression profiles constitute biological hypotheses for metazoan development
We illustrate the value of the reverse-engineering algorithm LeMoNe as a biological hypothesis generator for differential gene expression.
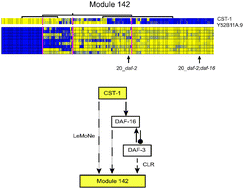
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1817-1830
https://doi.org/10.1039/B908108A
Inferring the transcriptional network of Bacillus subtilis
By integrating known and de novo predicted motifs with a comprehensive gene expression compendium, we expand the current Bacillus subtilis regulatory network and provide insight into its condition dependency.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1840-1852
https://doi.org/10.1039/B907310H
Analysis of structured and intrinsically disordered regions of transmembrane proteins
Intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) of helical bundle and beta barrel integral transmembrane proteins as well as the IDRs of water soluble proteins all exhibit statistically distinct amino acid compositional biases. This suggested that developing new predictors can increase the accuracy of disorder prediction for integral transmembrane proteins.
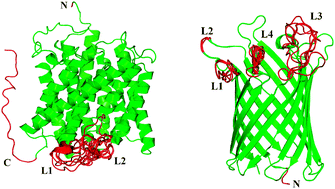
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1688-1702
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905913J
Prediction of protein –protein interactions between Helicobacter pylori and a human host
Interactions of extracellular protein domains in H. pylori with human proteins have been predicted. Analysis of some of the examples reveals that the interactions are consistent with the structural compatibility of binding partners. Examples of interactions with discernible biological relevance are discussed.
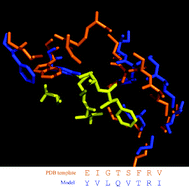
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1630-1635
https://doi.org/10.1039/B906543C
Towards inferring time dimensionality in protein–protein interaction networks by integrating structures: the p53 example
Structural data, efficient structural comparison algorithms and appropriate datasets and filters can assist in getting an insight into time dimensionality in interaction networks; in predicting which interactions can and cannot co-exist; and in obtaining concrete predictions consistent with experiment.
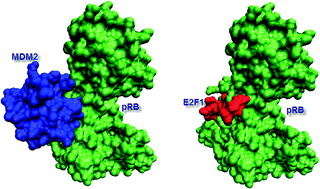
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1770-1778
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905661K
Stable G-quadruplexes are found outside nucleosome -bound regions
We show that regulatory G-quadruplexes found upstream of transcription start sites are located in a region depleted of nucleosomes. Generally in Caenorhabditis elegans and humans, stable G-quadruplexes are located outside nucleosome-bound regions, hence making it easier for them to form in vivo.
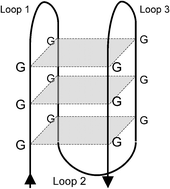
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1713-1719
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905848F
On the basic computational structure of gene regulatory networks
We extract the minimal core of causal relations, uncovering the hierarchical and modular organisation from a novel dynamical/causal perspective in a comparative study for Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene regulatory networks.
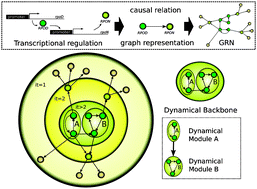
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1617-1629
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904960F
A dependency graph approach for the analysis of differential gene expression profiles
This paper describes the construction principles of a dependency network representing human protein coding genes integrating genomic, transcriptomic and proteomic profiles. We demonstrate the improved analysis of differential gene expression profiles at the level of this network.
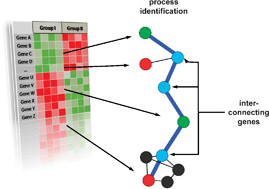
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1720-1731
https://doi.org/10.1039/B903109J
Genome -wide analysis predicts DNA structural motifs as nucleosome exclusion signals
Several factors are known to determine chromatin organization. Recent observations indicate a widespread role of G-quadruplexes, or G4 motifs, in gene regulation. Our results show a structural motif as a possible nucleosome exclusion signal and predict an alternate/additional regulatory role of G4 motifs.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1703-1712
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905132E
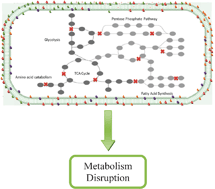
Strategies for efficient disruption of metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis from network analysis
Schematic illustration of metabolism in a mycobacterial cell. Network construction and graph analysis identifies strategic nodes for maximal and efficient disruption of metabolism, suggesting highly potent drug target combinations.
Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1740-1751
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905817F
Integration of signals from the B-cell antigen receptor and the IL-4 receptor leads to a cooperative shift in the cellular response axis
Crosstalk between signals emanating from two distinct cell surface receptors resulted in an additive effect on gene expression. Products of these genes then counteracted to fine-tune the cellular phenotypic response.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1661-1671
https://doi.org/10.1039/B901992H
DNA supercoiling regulates the stress-inducible expression of genes in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis
The genome-wide microarray analysis of stress-dependent gene expression due to changes in DNA supercoiling has been performed in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis. Gene expression profiles are presented for responses to cold, heat, and salt stresses.

Mol. BioSyst., 2009,5, 1904-1912
https://doi.org/10.1039/B903022K