Themed collection Berry Health Benefits Symposium

Symposium introduction: the eighth biennial berry health benefits symposium
Navindra P. Seeram and Britt Burton-Freeman introduce the Food & Function themed collection on the Berry Health Benefits Symposium.

Food Funct., 2020,11, 30-31
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO90063B
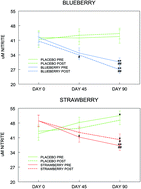
Effects of short-term consumption of strawberry powder on select parameters of vascular health in adolescent males
In both children and adults, dietary interventions strongly supports the concept that the regular consumption of strawberries can be associated with improvements in cardiovascular health.

Food Funct., 2020,11, 32-44
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO01844A
Berry polyphenols metabolism and impact on human gut microbiota and health
Berries are rich in phenolic compounds such as phenolic acids, flavonols and anthocyanins.
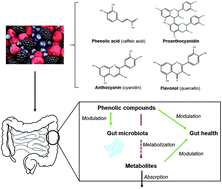
Food Funct., 2020,11, 45-65
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO01634A
Blueberries and cardiovascular disease prevention
Concept of how blueberries mediate vascular effects via modulation of cellular function by circulating anthocyanin metabolites.
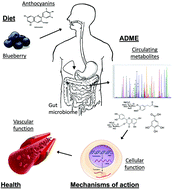
Food Funct., 2019,10, 7621-7633
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO02291K
Dietary berries, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: an overview of human feeding trials
This review focuses on the role of dietary berries, especially the commonly consumed blueberries, cranberries and strawberries on metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes in human trials.
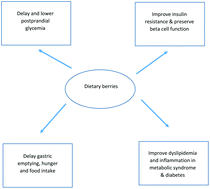
Food Funct., 2019,10, 6227-6243
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO01426H
Formulation of protein–polyphenol particles for applications in food systems
Consumers are demanding healthy nutritious foods rich in protein (both plant and animal) and biologically-active phytochemicals from plants, which can help the body to sustain a stronger immune system and fight against oxidative stress.

Food Funct., 2020,11, 5091-5104
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0FO00186D
The cognitive effects of an acute wild blueberry intervention on 7- to 10-year-olds using extended memory and executive function task batteries
In two separate experiments, children were tested on memory and executive function task batteries. Shorter memory reaction times were observed on the visuo-spatial grid task and short executive function times were observed on congruent trials of the attention network task.
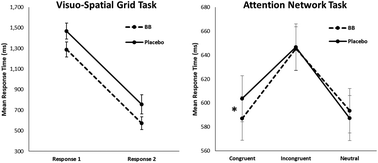
Food Funct., 2020,11, 4793-4801
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO02284H
A new category-specific nutrient rich food (NRF9f.3) score adds flavonoids to assess nutrient density of fruit
Nutrient profiling (NP) models, intended to capture the full nutritional value of plant-based foods, ought to incorporate bioactive phytochemicals, including flavonoids, in addition to standard nutrients.
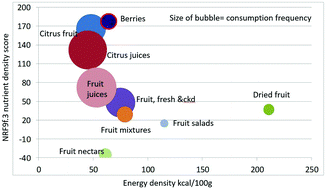
Food Funct., 2020,11, 123-130
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO02344E
Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa cv. Romina) methanolic extract promotes browning in 3T3-L1 cells
The conversion of white adipocytes to brown-like adipocytes by pharmacological and dietary compounds has gained attention as an effective strategy to fight obesity.
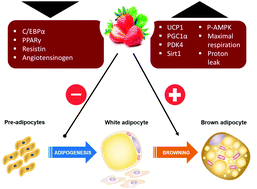
Food Funct., 2020,11, 297-304
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO02285F
Non-extractable polyphenols from cranberries: potential anti-inflammation and anti-colon-cancer agents
Both extractable and non-extractable polyphenol (NEP) rich fractions from cranberries were bioactive and the NEP-rich fraction showed promising anti-inflammation and anti-colon cancer potential.
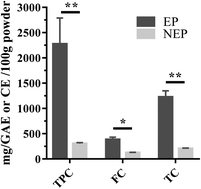
Food Funct., 2019,10, 7714-7723
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO01536A
The effects of blueberry and strawberry serum metabolites on age-related oxidative and inflammatory signaling in vitro
Berry fruits contain a variety of bioactive polyphenolic compounds that exhibit potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities.
Food Funct., 2019,10, 7707-7713
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO01913H
Inhibitory effects of cranberry polyphenol and volatile extracts on nitric oxide production in LPS activated RAW 264.7 macrophages
Cranberry volatiles have received little attention for health-promoting properties.
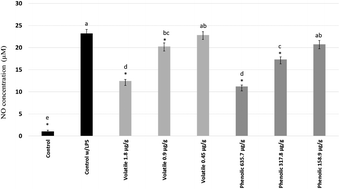
Food Funct., 2019,10, 7091-7102
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO01500K
Isolation of strawberry anthocyanin-rich fractions and their mechanisms of action against murine breast cancer cell lines
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of strawberry anthocyanin extract treatment on two in vitro models of murine breast cancer cell lines, in an attempt to detect a specific pathway through which strawberries exert anticancer activity.

Food Funct., 2019,10, 7103-7120
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO01721F
Dietary cranberry suppressed colonic inflammation and alleviated gut microbiota dysbiosis in dextran sodium sulfate-treated mice
Oral administration of freeze-dried whole cranberry powder via diet inhibited colitis in dextran sodium sulfate-treated mice, which was associated with modification of gut microbiota.
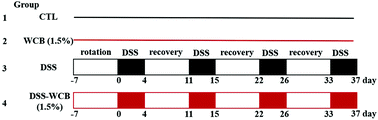
Food Funct., 2019,10, 6331-6341
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO01537J
Comparison of berry juice concentrates and pomaces and alternative plant proteins to produce spray dried protein–polyphenol food ingredients
Plant protein sources – buckwheat flour alone or blended with pea and rice proteins, and polyphenol sources – blueberry, cranberry and muscadine grape extracts from juice concentrates and pomaces – were complexed to obtain spray dried food ingredients.

Food Funct., 2019,10, 6286-6299
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO01587F
About this collection
This collection, Guest Edited by Navindra Seeram and Britt Burton Freeman, features selected articles from the 8th Biennial Berry Health Benefits Symposium, held in Portland, OR, USA, May 7-9, 2019, showcasing research into how berries positively impact human health. Sessions at the symposium covered cancer, leukaemia, diabetes, gut health, metabolism, brain aging, heart health and more. New articles will be added to this collection as they are published.
Also of interest
Anthocyanins from Natural Sources: Exploiting Targeted Delivery for Improved Health
Series: Food Chemistry, Function and Analysis
Editors: Marianne Su-Ling Brooks, Giovana B Celli
Interest in anthocyanins has increased in the past few years, due to their potential health-promoting properties as dietary antioxidants. Previously they were known as an important class of natural colorant, orange-red to blue-violet, found in fruits such as berries and in vegetables. This book discusses ways of targeting the delivery of these compounds, through manipulation of exploitation mechanisms. It addresses all aspects from extraction of anthocyanins from natural sources, their health benefits and metabolism to specialized controlled release applications. It will serve as a unique reference for those specializing in the fate of anthocyanins in the body (pharmacokinetics) and the research related to controlled release systems. It will provide an insight for pharmaceutical scientists, food engineers, food scientists and those interested in human health and nutrition.
https://doi.org/10.1039/9781788012614