Themed collection Physical chemistry of aerosols

Physical chemistry of aerosols
This special issue provides an overview of the state-of-the-art of research in the field of aerosol science.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7759-7759
https://doi.org/10.1039/B916865F
Reactions at surfaces in the atmosphere: integration of experiments and theory as necessary (but not necessarily sufficient) for predicting the physical chemistry of aerosols
This Perspective article gives a personal outlook on some chemistry occurring at the interface between air and condensed phases of potential atmospheric importance.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7760-7779
https://doi.org/10.1039/B906540G
Structural stability of electrosprayed proteins : temperature and hydration effects
Simulations of proteins in vacuum show that a water layer corresponding to 3 μm preserves the protein structure, even at temperatures as high as 425 K.
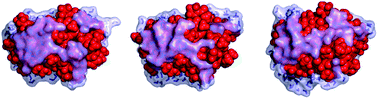
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 8069-8078
https://doi.org/10.1039/B903846A
Cloud condensation nuclei and ice nucleation activity of hydrophobic and hydrophilic soot particles
Low temperature freezing of soot depends on hydrophilicity and hygroscopicity.
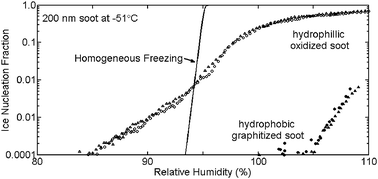
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7906-7920
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905334B
IR spectroscopy of physical and chemical transformations in cold hydrogen chloride and ammonia aerosols
When HCl and NH3 are injected into a collisional cell at 80 K, the pressure of N2 buffer gas determines whether homogeneous particle formation or the chemical reaction to produce NH4Cl dominates.
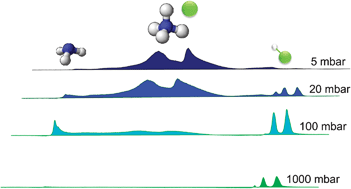
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7853-7860
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905425C
Homogeneous ice freezing temperatures and ice nucleation rates of aqueous ammonium sulfate and aqueous levoglucosan particles for relevant atmospheric conditions
Homogeneous ice nucleation from aqueous (NH4)2SO4 and levoglucosan particles is determined as a function of temperature and water activity.
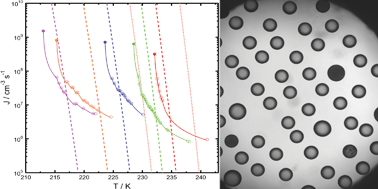
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 8056-8068
https://doi.org/10.1039/B903750K
Dynamics and mass accommodation of HCl molecules on sulfuric acid –water surfaces
A molecular beam technique has been used to study the dynamics and mass accommodation of HCl molecules in collision with sulfuric acid/water surfaces.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 8048-8055
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904629A
Reactivity of oleic acid in organic particles: changes in oxidant uptake and reaction stoichiometry with particle oxidation
Simultaneous measurement of oleic acid and ozone decay reveals stoichiometry considerably exceeding that of the primary and known secondary reactions.
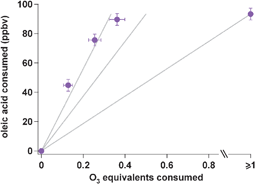
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7951-7962
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904285G
DRIFTS studies on the photodegradation of tannic acid as a model for HULIS in atmospheric aerosols
In situ and surface-sensitive spectroscopy of solid tannic acid photodegradation, the structure of adsorbed water before and after photodegradation and the hydrophilicity change as a result.
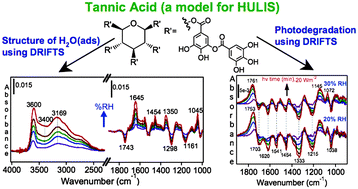
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7838-7847
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905236D
Reactive uptake studies of NO3 and N2O5 on alkenoic acid, alkanoate, and polyalcohol substrates to probe nighttime aerosol chemistry
NO3 and N2O5 reactive uptake coefficients were determined for five organic compounds to determine the atmospheric relevance of these heterogeneous reactions.
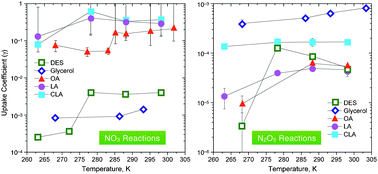
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7792-7803
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904741G
Deliquescence behaviour and crystallisation of ternary ammonium sulfate /dicarboxylic acid /water aerosols
Surface aerosols microscope (SAM) developed and utilised for quantitative investigations of single and multi-step deliquescence of internally mixed ternary aerosols.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7976-7984
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905007H
Tandem ion mobility-mass spectrometry (IMS-MS ) study of ion evaporation from ionic liquid -acetonitrile nanodrops
Ion evaporation kinetics of ionic liquids are studied using a parallel-plate differential mobility analyzer coupled to a time-of-flight mass spectrometer.
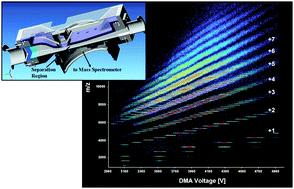
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 8079-8090
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904022F
Laboratory study of the interaction of HO2 radicals with the NaCl, NaBr, MgCl2·6H2O and sea salt surfaces
H2O2 was observed as a main product of HO2 interaction with salt surface indicating a heterogeneous HO2 self reaction mechanism.
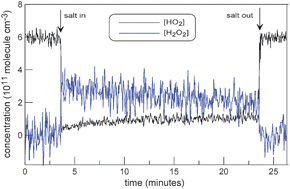
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7896-7905
https://doi.org/10.1039/B906300E
Laboratory chamber studies on the formation of organosulfates from reactive uptake of monoterpene oxides
Monoterpene oxides, rather than aldehydes or alcohols, are identified as important precursors in the formation of atmospherically relevant monoterpene organosulfates.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7985-7997
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904025K
Spectroscopic evidence for cyclical aggregation and coalescence of molecular aerosol particles
Formation of an aerosol from co-mixtures of CO2 and H2O in He(g) may lead to nucleation and isolation of primary CO2 particles on aggregates of water–ice particles.
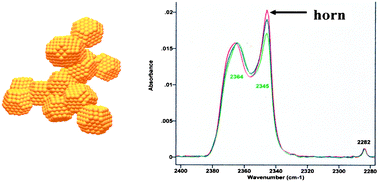
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7819-7825
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905018N
Using optical landscapes to control, direct and isolate aerosol particles
An optically trapped aerosol particle can be isolated from a flow of aerosol by encircling it with a light scattering ring.
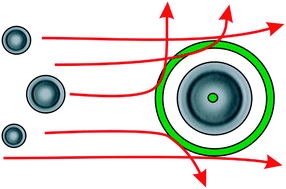
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 8015-8020
https://doi.org/10.1039/B908270K
Time-resolved molecular characterization of limonene /ozone aerosol using high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
High-resolution mass spectrometry simultaneously detects hundreds of condensable organic species during the course of reaction between limonene and ozone.
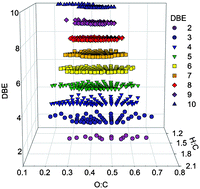
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7931-7942
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905288G
Effective broadband refractive index retrieval by a white light optical particle counter
A new approach to retrieve the effective broadband refractive indices of aerosols by a white light aerosol spectrometer is presented.
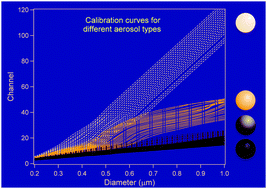
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7943-7950
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905292E
Measurements and simulations of the near-surface composition of evaporating ethanol –water droplets
Using cavity enhanced Raman scattering, we probe the evolving gradient in near-surface composition during the evaporation of a multicomponent droplet.
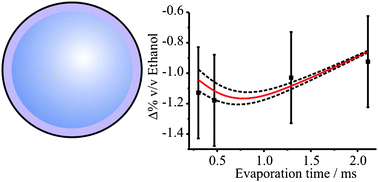
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7780-7791
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904070F
Influence of gas-to-particle partitioning on the hygroscopic and droplet activation behaviour of α-pinene secondary organic aerosol
The degree of oxidation of secondary organic aerosol has less effect on droplet activation than previously anticipated.
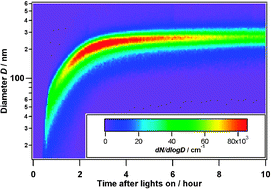
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 8091-8097
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904162A
Measurement of fragmentation and functionalization pathways in the heterogeneous oxidation of oxidized organic aerosol
Fundamental changes to the composition of model organic aerosols upon heterogeneous oxidation were monitored using high-resolution electron-impact aerosol mass spectrometry.
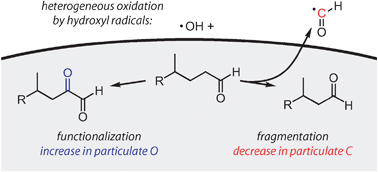
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 8005-8014
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905289E
A study of oleic acid and 2,4-DHB acid aerosols using an IR-VUV-ITMS: insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the technique
Fragmentation of metastable molecular ions during storage in an ITMS can reduce some of the benefits of using a soft ionization technique for single particle measurements.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7963-7975
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904748D
Water uptake of clay and desert dust aerosol particles at sub- and supersaturated water vapor conditions
Characterization of the interaction between water vapor and atmospheric mineral particles as a function of size, composition, and generation method.
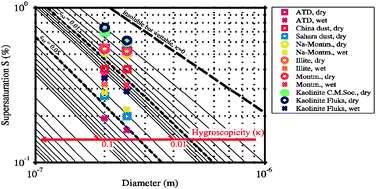
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7804-7809
https://doi.org/10.1039/B901585J
Effects of dicarboxylic acid coating on the optical properties of soot
Enhancement in the optical properties of soot by transparent coatings is strongly related to the ability of the coating materials to change the morphology of soot aggregates.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7869-7875
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904129J
Quantifying the reactive uptake of OH by organic aerosols in a continuous flow stirred tank reactor
We report a new method for measuring the heterogeneous chemistry of sub-micron organic aerosol particles using a continuous flow stirred tank reactor.
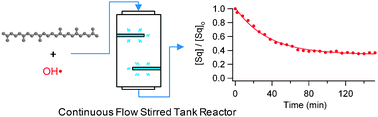
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7885-7895
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904418C
Infrared spectroscopy of ozone and hydrogen chloride aerosols
Liquid aerosols of ozone have been generated in a collisional cooling cell and measured by FTIR spectroscopy.
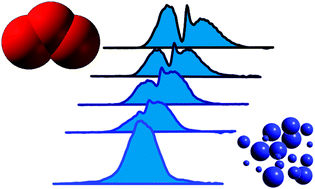
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7848-7852
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905424N
Kinetics of the heterogeneous conversion of 1,4-hydroxycarbonyls to cyclic hemiacetals and dihydrofurans on organic aerosol particles
A kinetic model was developed to describe the heterogeneous conversion of 1,4-hydroxycarbonyls to cyclic hemiacetals and dihydrofurans in atmospheric aerosol particles.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 8029-8039
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904333K
Secondary organic aerosol formation from multiphase oxidation of limonene by ozone : mechanistic constraints via two-dimensional heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy
Heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) spectroscopy of secondary organic aerosol from limonene ozonolysis clearly identifies residual terminal unsaturations.
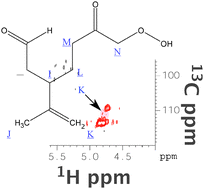
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7810-7818
https://doi.org/10.1039/B820005J
Mid-infrared complex refractive indices for oleic acid and optical properties of model oleic acid /water aerosols
Refractive indices for oleic acid are reported and used to model core–shell aerosol properties.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7998-8004
https://doi.org/10.1039/B905371A
Formation of naproxen –polylactic acid nanoparticles from supercritical solutions and their characterization in the aerosol phase
PLA-coated naproxen particles are formed as aerosols by rapid expansion of supercritical carbon dioxide solutions.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7861-7868
https://doi.org/10.1039/B901744E
Photoenhanced ozone loss on solid pyrene films
Actinic radiation enhances the uptake of ozone by solid pyrene films and, to a lesser extent, the loss of pyrene itself.
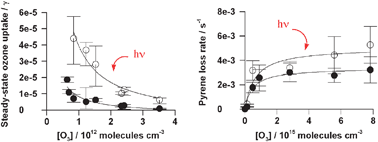
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7876-7884
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904180J
Timescale for hygroscopic conversion of calcite mineral particles through heterogeneous reaction with nitric acid
Modelled change in hygroscopicity of calcite mineral particles following heterogeneous reaction with nitric acid vapour derived from flow tube experiments.
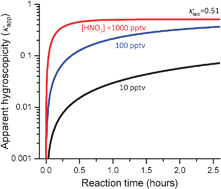
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7826-7837
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904217B
Surface tension of mixed inorganic and dicarboxylic acid aqueous solutions at 298.15 K and their importance for cloud activation predictions
Erroneous surface tension models of inorganic–organic mixtures cause bigger discrepancies in CCN activation predictions than the inorganic to organic ratio.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 8021-8028
https://doi.org/10.1039/B906849J
Organic nitrate formation in the radical-initiated oxidation of model aerosol particles in the presence of NOx
Organic nitrates are observed from the oxidation of solid (but not liquid) brassidic acid aerosols in the presence of NO with implications for the chemical transformation of organic aerosols in the atmosphere.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 8040-8047
https://doi.org/10.1039/B909239K
Kinetics of the heterogeneous reaction of nitric acid with mineral dust particles: an aerosol flowtube study
We present a detailed kinetic data set for the reaction of Arizona test dust with HNO3(g).

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009,11, 7921-7930
https://doi.org/10.1039/B904290N