Themed collection Analytical methods for a low resource world

Recent advances in screen-printed carbon electrodes for food additive analysis
Screen-printed carbon electrode is a option of analytical device for additive analysis in food samples; however, the sample preparation, selectivity, and detectability are key challenges to overcome.

Anal. Methods, 2025,17, 3613-3628
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5AY00236B
A portable and ecological paper-based device for glucose monitoring in peripheral blood mononuclear cell lysates
The increasing need for point-of-care (POC) testing has prompted a rise in the popularity of affordable biosensors that are eco-friendly, especially paper-based electrochemical sensors.

Anal. Methods, 2025,17, 2529-2535
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5AY00057B
A colour sensor integrated into a microcontroller platform as a reliable tool for measuring pH changes in biochemistry applications
An open-source colorimeter with a colour sensor for determination of pH in liquids with a universal indicator – a novel approach for reaction monitoring.

Anal. Methods, 2024,16, 6487-6493
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4AY00637B
Designing a locally produced DENV-1 nucleic acid diagnostic for low resource regions with endemic disease
Recombinant local-production of innovative silica bound RT-LAMP enzymes, extends shelf-life for use in endemic Dengue diagnostic, using novel DENV-1 primer-set.

Anal. Methods, 2025,17, 8489-8501
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5AY00889A
A paper-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay coupled with a portable heating device for point-of-care detection of syphilis in low-resource settings
A paper-based LAMP assay integrated with a portable heating device enables rapid, low-cost, and point-of-care detection of Treponema pallidum in resource-limited settings.

Anal. Methods, 2025,17, 7420-7430
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5AY00749F
A DoE-guided development and validation of a novel HPLC method for determining N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase activity via p-nitroaniline quantification
This work concerns the development, optimization, and validation of a cost-effective high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method for measuring NAM-amidase activity by detecting its enzymatic product, p-nitroaniline.

Anal. Methods, 2025,17, 3963-3975
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5AY00310E
Towards the development of an alternative analysis method to determine lead in eyeliner cosmetics
Development of a safe citric acid extraction method for potentially toxic elements in cosmetics, followed by field-friendly and quantitative anodic stripping voltammetry analysis using an inexpensive stencil printed carbon electrode (SPCE).

Anal. Methods, 2025,17, 4009-4017
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5AY00389J
A paper-based analytical device for rapid colorimetric detection of aluminium in aerosol antiperspirants
This work focuses on developing a simple and low-cost methodology for colorimetric analysis of aluminum in aerosol antiperspirants using paper-based analytical devices.

Anal. Methods, 2025,17, 3976-3984
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5AY00229J
Low-cost and portable 3D-printed sensor for the determination of secnidazole in pharmaceutical and seized drug samples
Additive manufacturing (3D printing), particularly fused deposition modeling (FDM), has rapidly advanced, offering customized designs, reduced waste, lower costs, and fast prototyping for electroanalytical applications.

Anal. Methods, 2025,17, 2038-2045
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4AY02096K
Rapid determination of chemical losses in a microplate bioassay using fluorescence spectroscopy
A novel fluorescence spectroscopy method that can be used as a low resource, rapid, and green approach for measuring chemical losses in polystyrene microplates commonly used in bioassays.

Anal. Methods, 2025,17, 514-524
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4AY01980F
Low-cost, real-time detection of bacterial growth via diffraction-based sensing
A low-tech, low-cost method for real-time, rapid bacterial growth detection using diffractive elements made from live bacteria.

Anal. Methods, 2024,16, 8366-8371
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4AY01489H
Label-free impedimetric analysis of microplastics dispersed in aqueous media polluted by Pb2+ ions
A label-free method based on dielectric impedance spectroscopy was developed for the differentiation of virgin from Pb2+ polluted microplastics.

Anal. Methods, 2024,16, 7654-7666
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4AY01324G
A cheap and straightforward method for the selective isolation of histidine-derived natural products using nickel(II) phosphate
Using a simple three step solid-phase extraction protocol with nickel(II) phosphate, two histidine-derived alkaloids were isolated from fungal cultures.

Anal. Methods, 2024,16, 7015-7020
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4AY01467G
Chromatographic fingerprinting of epiphytic fungal strains isolated from Withania somnifera and biological evaluation of isolated okaramine H
Investigation of epiphytic strains of Withania somnifera using chromatographic techniques to study chemical diversification, with isolation and structure elucidation of okaramine H from Aspergillus aculeatus.

Anal. Methods, 2024,16, 5943-5953
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4AY00901K
A LAMP-based hydrogen ion selective electrochemical sensor for highly sensitive detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Simple, rapid, and accurate detection of M. pneumonia was achieved using a portable handheld POCT platform, with the entire testing process being completed within 30 minutes.

Anal. Methods, 2024,16, 3020-3029
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4AY00341A
A simplified lateral flow immunosensor for the assay of carcinoembryonic antigen in low-resource settings
A colorimetric lateral flow immunosensor is developed and validated for assay of carcinoembryonic antigen in serum at the point-of-care (POC) or in resource-limited settings.

Anal. Methods, 2024,16, 2921-2929
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4AY00381K
Distance-based detection of paracetamol in microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for forensic application
Whisky adulteration is a prevalent practice driven by the high cost of these beverages.

Anal. Methods, 2024,16, 33-39
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3AY01739G
Development of a paper-based lateral flow prothrombin assay
Devices fabricated using chromatography paper and wax printing, modified with thromboplastin (top left). Distance travelled by plasma samples (bottom right) is proportional to hospital prothrombin time (PT) (main graph) from normal (green) to significantly prolonged (red).
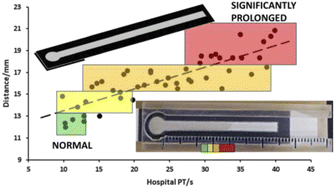
Anal. Methods, 2022,14, 3718-3726
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2AY00965J
Homebuilt cost-effective nitrogen blowdown evaporator
A nitrogen blowdown evaporator built with widely-available materials and techniques is described, accompanied by plans and detailed instructions for assembly. We show that the apparatus operates without causing contamination or sample loss.

Anal. Methods, 2025,17, 1930-1935
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4AY02118E
About this collection
This collection addresses new approaches to the application of analytical methods that enhance or improve their access in low-resource settings. It highlights how many scientists, technologists and engineers are turning away from traditional technological complexity to instead apply ‘low-tech’ approaches which can achieve comparable outcomes without the need for associated infrastructural complexity. This so-called ‘frugal innovation’ is taking creative approaches to eliminating technological complexity in the materials, production methods, analytical approaches and usage of such technologies, which allows their application in resource-limited situations, and is often now also addressing issues of environmental sustainability.
Guest Edited and curated by Tony Killard (University of the West of England, UK), Stefano Cinti (University of Naples Federico II, Italy) and Anthony Gachanja (Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, Kenya), the collection is open to new submissions from all areas of analytical chemistry and new articles will be added as they are published