Immobilization of bio-macromolecules on self-assembled monolayers: methods and sensor applications
Abstract
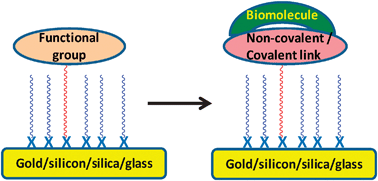
Attachment of biomolecules on gold, silicon or glass surfaces has direct implications for the development of novel biosensors in the context of nanoscale detection of pathogens and other

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...