Core–shell Ag@polypyrrole for synchronous pre-enrichment and immobilization of iodine (I−, IO3−) from liquid radioactive wastes†
Abstract
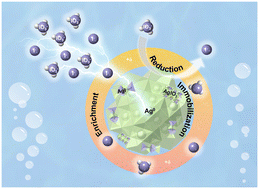
Radioiodine is of great concern owing to its high mobility in the environment and long-term radiotoxicity, and effective techniques for the simultaneous removal of iodide (I−) and iodate (IO3−) from aqueous solutions remain a significant challenge. Here, Ag@polypyrrole core–shell nanoparticles (Ag@PPy) were synthesized in situ and constructed by synergistic enrichment and immobilization as a desirable iodine nano-adsorbent. Its performance benefits from the ability for anions to be pre-enriched on the surface of Ag@PPy via electrostatic force through the positively charged polypyrrole with nitrogen-containing groups and then immobilized in the core–shell nanostructure with nanosilver as a reactive center. These efforts gave rise to Ag@PPy exhibiting an ultrahigh iodide adsorption capacity (788.7 mg g−1) and desirable iodate uptake capacity (133.9 mg g−1). More importantly, in the low-concentration region, Ag@PPy is able to almost completely remove I− and IO3− from aqueous solution even in the presence of competitive anions such as Cl−, SO42−, NO3− and CO32−, with a distribution coefficient Kd of up to 3.90 × 105 and 2.30 × 105 mL g−1, respectively. Unexpectedly, this core–shell nanostructure endows silver-based materials with high stability under acid–base conditions, and reduces the leaching rate approximately 10-fold compared to silver powder at near-neutral pH. This work highlights the feasibility of using Ag-containing nanomaterials to separate radioiodine from liquid environments.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanomaterial applications in water


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...