Engineering probiotics-derived membrane vesicles for encapsulating fucoxanthin: evaluation of stability, bioavailability, and biosafety†
Abstract
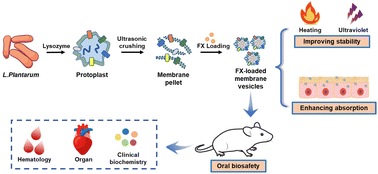
Due to the multiplex absorption barrier in the gastrointestinal tract, the low oral bioavailability of many lipophilic chemicals limits their range of applications. Biomimetic nanovesicles offered unique advantages in overcoming multiple barriers to oral absorption and improving the oral bioavailability of encapsulated water-insoluble compounds. Here, we report an engineering preparation strategy of synthetic probiotic membrane vesicles for encapsulating fucoxanthin. Fucoxanthin-loaded synthetic membrane vesicles (FX-MVs) were spherical with a particle size of 412 nm. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and ultraviolet–visible absorption spectroscopy results revealed that fucoxanthin was successfully doped into the membrane vesicles. Moreover, FX-MVs improved the stability of fucoxanthin under heating and UV irradiation conditions. In vitro experiments indicated that FX-MVs could effectively promote the cell uptake, and the mechanism mainly involved endocytosis. Simultaneously, ex vivo experiments confirmed that FX-MVs enhanced intestinal retention. Finally, the oral biosafety of FX-MVs was evaluated. The mice fed FX-MVs did not show toxicity signs and adverse effects, based on the results of clinical observation, body weight, hematology, clinical biochemistry, and organ pathology. Altogether, these results suggest that synthetic probiotic membrane vesicles can be used as safe delivery carriers to improve the stability and bioavailability of hydrophobic food bioactive ingredients.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function HOT Articles 2023


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...