Influence and effect mechanism of filler type on the physicochemical properties, microbial numbers, and digestibility of ovalbumin emulsion gels during storage
Abstract
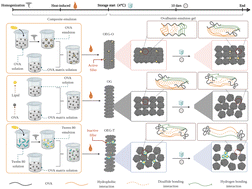
This study was designed to investigate the influence and effect mechanism of the filler type on the physicochemical properties, microbial numbers, and digestibility of ovalbumin emulsion gels (OEGs) during storage. Sunflower oil was emulsified with ovalbumin (20 mg mL−1) and Tween 80 (20 mg mL−1) separately to prepare ovalbumin emulsion gels (OEGs) that contained active and inactive fillers, respectively. The formed OEGs were stored at 4 °C for 0, 5, 10, 15, and 20 days. The active filler enhanced the gel hardness, water holding capacity, fat holding capacity, and surface hydrophobicity and decreased the digestibility and free sulfhydryl content during storage compared to control (unfilled) ovalbumin gel, whereas the inactive filler had the opposite effects. Protein aggregation diminished, lipid particle aggregation increased, and the amide A band shifted to a higher wavenumber for all three types of gel during storage, suggesting that the compact network structure of the OEG became rough and disordered with storage. The OEG with the active filler did not inhibit microbial growth, and the OEG with the inactive filler did not significantly promote the development of bacteria. In addition, the active filler delayed the in vitro digestion of the protein in the OEG throughout storage. Emulsion gels containing active filler facilitated the retention of the gel properties during storage, whereas emulsion gels containing inactive filler exacerbated the loss of the gel properties during storage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...