Maternal yogurt consumption during pregnancy and infantile eczema: a prospective cohort study†
Abstract
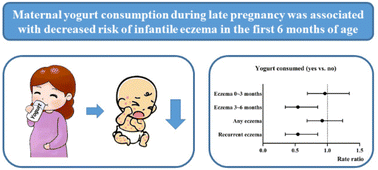
Maternal fermented food consumption during pregnancy was suggested to be beneficial for a healthy microbiome, and prevent infantile eczema. However, the association between yogurt and eczema has not been well investigated. To examine whether maternal yogurt consumption during pregnancy is associated with risk of infantile eczema, we performed a prospective mother–offspring cohort study in Wuhan, China. Maternal yogurt consumption in late pregnancy was assessed with a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire. The main outcomes were doctor-diagnosed infantile eczema collected at 3 and 6 months postpartum. Adjusted rate ratios (aRRs) were calculated by Poisson regression models adjusted for potential confounders. In our study, 182 (7.7%) of 2371 infants followed for 3 months and 84 (4.0%) of 2114 infants followed until 6 months reported doctor-diagnosed eczema. Compared to infants whose mothers had not consumed any yogurt, infants with mothers who consumed yogurt during late pregnancy had reduced risk of eczema between 3 and 6 months of age (aRR = 0.54, 95% CI 0.35–0.85); the reduction was pronounced in those with maternal yogurt intake >3 times per week (aRR = 0.48, 95% CI 0.28–0.82) and >50 g day−1 (aRR = 0.50, 95% CI 0.30–0.81). Moreover, infants with mothers who consumed yogurt showed decreased risk for recurrent eczema within the first 6 months (aRR = 0.46, 95% CI 0.22–0.98). In conclusion, this study found that maternal yogurt consumption during late pregnancy was related to a reduced incidence of eczema in infants aged 3 to 6 months, and recurrent eczema in the first 6 months of life.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function HOT Articles 2023


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...