Response of wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv.) seedlings to combined effects of polystyrene nanoparticles and tetracycline†
Abstract
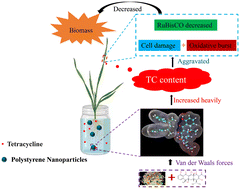
Micro(nano)plastic and antibiotic pollution is occurring worldwide. However, information on the potential threat of pollution to terrestrial plants is limited. Consequently, this research aimed to determine the individual and combined effects of polystyrene nanoplastics (PS NPs) and tetracycline (TC) on wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv.) seedlings. The combined effects of PS NPs and TC on wheat seedlings were investigated using a hydroponic system to avoid the influence of other environmental factors. The results showed that TC could be absorbed by the wheat roots, migrate upward, and accumulate in the shoots. Additionally, TC accumulation stimulated the production and accumulation of superoxide anions (O2˙−) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the shoots and roots. This inhibited the photosynthesis process by reducing ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase activity and chlorophyll content, decreasing the dry weight of wheat. An increase in the O2˙− and H2O2 content induced superoxide dismutase and catalase activity to alleviate oxidative damage. Notably, the presence of the PS NPs significantly increased the TC content by 31.3–94.4% and 3.19–92.0% in the wheat shoots and roots, respectively. This may be because TC was loaded onto the PS NPs through van der Waals forces, and they entered the wheat seedlings and aggravated the negative effects of TC, leading to cell lipid peroxidation. Although organelle damage was not observed, the separation of the cell wall and membrane was more serious in the shoots and roots exposed to the combined treatments than in the individual TC or PS NP treatments. Therefore, the presence of the PS NPs negatively influenced wheat seedlings and aggravated the damage induced by TC. Thus, the potential risk of the combined effects of PS NPs and TC on plants and human health should be of great concern.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Science: Nano Recent HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...