New insight into environmental oxidation of phosmet insecticide initiated by HO˙ radicals in gas and water – a theoretical study†
Abstract
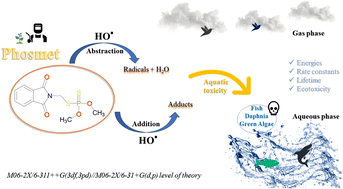
Phosmet is an organophosphorus insecticide widely used in agriculture to control a range of insects; recently, it was banned by the European Union in 2022 due to its harmful effects. However, its environmental degradation and fate have not yet been evident. Thus, phosmet oxidation by HO˙ radicals was theoretically studied in this work using the DFT approach at the M06-2X/6-311++G(3df,3pd)//M06-2X/6-31+G(d,p) level of theory. Three different mechanisms were considered, including formal hydrogen transfer (FHT), radical adduct formation (RAF), and single electron transfer (SET). The mechanisms, kinetics, and lifetime were studied in the gas and aqueous phases, in addition to its ecotoxicity evaluation. The results show that FHT reactions were dominant in the gas phase, while RAF was more favourable in the aqueous phase at 298 K, while SET was negligible. The branching ratio indicated that H-abstractions at the methyl and the methylene groups were the most predominant, while the most favourable HO˙-addition was observed at the phosphorus atom of the dithiophosphate group. The overall rate constant values varied from 1.2 × 109 (at 283 K) to 1.40 × 109 M−1 s−1 (at 323 K) in the aqueous phase and from 6.29 × 1010 (at 253 K) to 1.32 × 1010 M−1 s−1 (at 323 K) in the gas phase. The atmospheric lifetime of phosmet is about 6 hours at 287 K, while it can persist from a few seconds to several years depending on the temperature and [HO˙] concentration in the aqueous environment. The QSAR-based ecotoxicity evaluation indicates that phosmet and its degradation products are all dangerous to aquatic organisms, although the products are less toxic than phosmet. However, they are generally developmental toxicants and mutagenicity-negative compounds.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Contaminant remediation and fate


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...