Designing hexaphyrins for high-potential NLO switches: the synergy of core-modifications and meso-substitutions†
Abstract
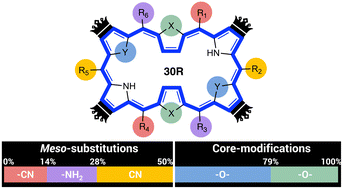
Due to the enormous size of the chemical compound space, usually only small regions are traversed with traditional direct molecular design approaches making the discovery for novel functionalized molecules for nonlinear optical applications challenging. By applying inverse molecular design algorithms, we aim to efficiently explore larger regions of the compound space in search of promising hexaphyrin-based molecular switches as measured by their first-hyperpolarizability (βHRS) contrast. We focus on the 28R → 30R switch with a functionalization pattern allowing for centrosymmetric OFF states yielding zero βHRS response. This switch is particularly challenging as full meso-substitution with a single type of functional group or core-modifications result in almost no contrast enhancement. We carried out four inverse design procedures during which two sets of core-modifications and three sets of meso-substitutions sites were systematically optimized. All 4 optimal switches are characterized by a mix of meso-substitutions and core-modifications, of which the best performing switch yields a 10-fold improvement over the parent macrocycle. Throughout the inverse design procedures, we collected and analyzed a database biased towards high NLO contrasts that contains 277 different patterns for hexaphyrin-based switches. We derived three design rules to obtain highly functional 28R → 30R NLO switches: (I) a combination of 2 strong EWG and 1 EDG group is the ideal recipe for increasing the NLO contrast, though their position also plays an important role. (II) The type of core-modification is less important when only the diagonal positions are core-modified. Switches with 4 core-modifications show a clear preference for oxygen. (III) Keeping centrosymmetry in the OFF state remains highly beneficial given the investigated functionalization pattern. Finally, we have demonstrated that combining meso-substitutions with core-modifications can synergistically improve the NLO contrast.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...