Identification of novel candidates for inhibition of LasR, a quorum-sensing receptor of multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, through a specialized multi-level in silico approach†
Abstract
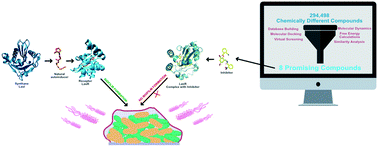
The emergence of multi-drug resistant bacteria in the past decades has become one of the major public health issues of our time. One of the main mechanisms of resistance and persistence of bacteria is their ability to form biofilms. Quorum-sensing (QS) is one of the main mechanisms of biofilm formation. Interfering with the QS cascade constitutes a non-antibiotic strategy to reduce biofilm formation and affect bacterial resistance. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, QS takes place by four different systems, which start with the activation of transcriptional receptor LasR. This receptor is stabilized by C12-HSL. In this work, we have optimized and employed a multi-level in silico protocol to identify promising LasR inhibitors, combining different computer aided drug design techniques such as molecular docking, virtual screening, molecular dynamics and free energy calculations. The protocol was optimized using all 21 available LasR X-ray structures, 7 docking scoring functions, and a library of 90 active and 4500 inactive compounds. The optimized protocol was used to scan 294 498 chemically distinct compounds from 5 different databases, of which 30 compounds were further studied by molecular dynamics and free energy calculations and resulted in 8 possible QS inhibitors with promising ADME properties and binding affinity.
- This article is part of the themed collection: MSDE Recent HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...