Intelligent nanoscope for rapid nanomaterial identification and classification†
Abstract
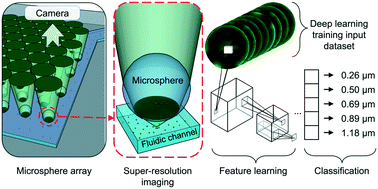
Machine learning image recognition and classification of particles and materials is a rapidly expanding field. However, nanomaterial identification and classification are dependent on the image resolution, the image field of view, and the processing time. Optical microscopes are one of the most widely utilized technologies in laboratories across the world, due to their nondestructive abilities to identify and classify critical micro-sized objects and processes, but identifying and classifying critical nano-sized objects and processes with a conventional microscope are outside of its capabilities, due to the diffraction limit of the optics and small field of view. To overcome these challenges of nanomaterial identification and classification, we developed an intelligent nanoscope that combines machine learning and microsphere array-based imaging to: (1) surpass the diffraction limit of the microscope objective with microsphere imaging to provide high-resolution images; (2) provide large field-of-view imaging without the sacrifice of resolution by utilizing a microsphere array; and (3) rapidly classify nanomaterials using a deep convolution neural network. The intelligent nanoscope delivers more than 46 magnified images from a single image frame so that we collected more than 1000 images within 2 seconds. Moreover, the intelligent nanoscope achieves a 95% nanomaterial classification accuracy using 1000 images of training sets, which is 45% more accurate than without the microsphere array. The intelligent nanoscope also achieves a 92% bacteria classification accuracy using 50 000 images of training sets, which is 35% more accurate than without the microsphere array. This platform accomplished rapid, accurate detection and classification of nanomaterials with miniscule size differences. The capabilities of this device wield the potential to further detect and classify smaller biological nanomaterial, such as viruses or extracellular vesicles.
- This article is part of the themed collections: AI in Microfluidics and Lab on a Chip HOT Articles 2022


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
