Focusing on a nickel hydrocorphinoid in a protein matrix: methane generation by methyl-coenzyme M reductase with F430 cofactor and its models
Abstract
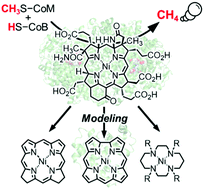
Methyl-coenzyme M reductase (MCR) containing a nickel hydrocorphinoid cofactor, F430, is an essential enzyme that catalyzes anaerobic methane generation and oxidation. The active Ni(I) species in MCR converts methyl-coenzyme M (CH3S–CoM) and coenzyme B (HS–CoB) to methane and heterodisulfide (CoM–S–S–CoB). Extensive experimental and theoretical studies focusing on the substrate-binding cavity including the F430 cofactor in MCR have suggested two principally different reaction mechanisms involving an organonickel CH3–Ni(III) species or a transient methyl radical species. In parallel with research on native MCR itself, the functionality of MCR has been investigated in the context of model complexes of F430 and recent protein-based functional models, which include a nickel complex. In the latter case, hemoproteins reconstituted with tetradehydro- and didehydrocorrinoid nickel complexes have been found to represent useful model systems that are responsible for methane generation. These efforts support the proposed mechanism of the enzymatic reaction and provide important insight into replicating the MCR-like methane-generation process. Furthermore, the modeling of MCR described here is expected to lead to understanding of protein-supported nickel porphyrinoid chemistry as well as the creation of MCR-inspired catalysis.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Trends and Challenges in Porphyrinoid Chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
