Sensitive analysis of phthalate esters in plastic bottled water via on-line capillary solid-phase microextraction liquid chromatography electrospray ionization-ion trap mass spectrometry†
Abstract
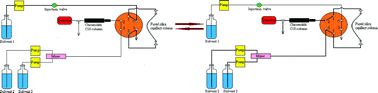
An online capillary solid-phase microextraction coupled liquid chromatography electrospray ionization-ion trap mass spectrometry (cSPME-LC-ESI-IT-MS) has been developed and applied for analyzing six phthalate esters (PAEs) in commercially available plastic bottled water. The extraction column was a Supel-Q PLOT fused silica capillary column. The optimal extraction time, extraction flow rate, desorption time, and desorption flow rate were 0.5 min, 0.1 mL min−1, 1 min, and 0.5 mL min−1, respectively. A green extraction eluent of deionized distilled water and the desorption eluent of acetonitrile/water (65/35, v/v) were used for the extraction–desorption process. The detection of six PAEs with on-line cSPME-LC-ESI-IT-MS was in positive mode. The limits of detection/quantification (LODs/LOQs) were from 0.07/0.22 to 0.17/0.55 ng mL−1 for the six target PAEs. The identification for the six PAEs in five different domestic brands of plastic bottled water was performed using the product ions of secondary MS. The analysis results showed that only di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) was found in two brands of plastic bottled water with an average concentration of 1.8 ng mL−1 and 1.6 ng mL−1, respectively. The intra- and inter-day precisions for DEHP analysis during a successive three-day measurement by the on-line cSPME-LC-ESI(+)-IT-MS were 4.8–7.1% and 11.1–12.5%, respectively. The analysis accuracy for the six PAEs in the plastic bottled water was in the range of 90.3–96.8%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...