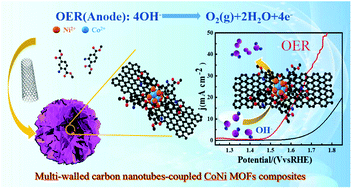
A novel multi-walled carbon nanotube-coupled CoNi MOF composite enhances the oxygen evolution reaction through synergistic effects†
Abstract
Optimizing the composition, structure, and carrier of non-noble-metal-based metal–organic framework (MOF) materials effectively improves their electrocatalytic performance. Recently, CoNi bimetallic MOFs have attracted attention for hydrogen production in alkaline water electrolysis devices. Unfortunately, the most common studies have focused on the control of the morphology and structure of the MOF itself, while ignoring the effects of the synergy between the MOF and the carrier or other conductive agents. In this work, a multi-walled carbon nanotube-coupled CoNi MOF composite (CoNi MOFs-mCNTs) was synthesized via a solvothermal method using multi-walled carbon nanotubes (mCNTs) as a shape-directing agent and its application was explored for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) in alkaline solution. The electrochemical test results demonstrate that, compared with commercial RuO2 (CM-RuO2) and a CoNi MOF without mCNTs, the CoNi MOFs-mCNTs with optimal mCNTs content show improved OER activity and durability. Physical characterization indicates that the structure and electronic properties of the CoNi MOFs-mCNTs are primarily influenced by the mCNTs, which conveys that CoNi MOFs-mCNTs with a high specific surface area exhibit improved OER activity in alkaline solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...