Ambient N2-to-NH3 fixation over a CeO2 nanoparticle decorated three-dimensional carbon skeleton†
Abstract
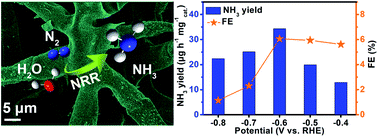
Electrochemical N2 reduction emerges as a promising substitute to the Haber–Bosch process for ambient NH3 synthesis, but it is a tough task to develop efficient catalysts. Here, we propose a CeO2 nanoparticle decorated three-dimensional carbon skeleton derived from Juncus as an active and stable electrocatalyst for N2-to-NH3 conversion. In N2-saturated 0.1 M Na2SO4, this nanohybrid attains a large NH3 yield of 33.4 μg h−1 mgcat.−1 with a faradaic efficiency of 6.1% at −0.6 V vs. the reversible hydrogen electrode. Furthermore, it also possesses favorable durability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...