Remote C(sp3)–H functionalization via catalytic cyclometallation: beyond five-membered ring metallacycle intermediates
Abstract
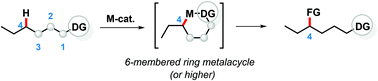
Despite impressive recent momentum gained in C(sp3)–H activation, achieving high regioselectivity in molecules containing different C–H bonds with similar high energy without abusing tailored substitution remains as one of the biggest challenges. The use of directing groups, especially those featuring bidentate coordination, typically in combination with palladium catalysis, has fueled the development of a number of direct C(sp3)–H bond functionalizations via cyclometallation. In most of the reported examples, the regioselectivity is determined by the strong propensity of PdII to form square planar five-membered metalacycles. In contrast, targetting C–H bonds that are farther than three bonds away from the coordinating heteroatom through the intermediacy of less favorable six-membered (or higher) metalacycles is far more difficult. In fact, achieving high selectivity via six-membered metalacycles without blocking the competitive functionalization via a five-membered metalacycle represents an even more difficult challenge. This review provides an overview of methods enabling catalytic C(sp3)–H activation via six-membered metalacycle intermediates, with an emphasis on mechanistic aspects regarding the control of regioselectivity and strategies towards disfavoring the formation of the five-membered palladacycle in preference for the six-membered analog.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Organic Chemistry Frontiers Review-type Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...