Graphdiyne–hemin-mediated catalytic system for wound disinfection and accelerated wound healing†
Abstract
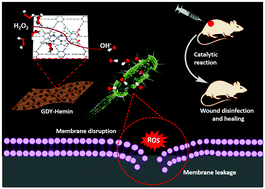
Surgical site infections are the most common and serious concern in health care settings. Currently, systemic administration of prophylactic antibiotics or local disinfection treatment is prescribed after surgical procedures. However, prolonged use of antibiotics may pose adverse side effects, bacterial resistance and hospitalization costs. Recently, the use of nanomaterials with peroxidase enzyme-mimic activity has drawn higher consideration due to their high antibacterial potential and minimum biotoxicity. Hemin is a highly active molecule and also the active source of many biological enzymes, such as peroxidase, which could efficiently catalyze various biochemical reactions. However, the insolubility of hemin makes it easy for it to aggregate and lose its catalytic ability. Here, we designed a well-dispersed hemin/graphdiyne (GDY) nanocomposite (GDY–hemin) with high peroxidase activity. GDY–hemin can decompose hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to generate highly-toxic hydroxyl radicals that impair bacterial cell membranes, ultimately leading to bacterial death in both in vitro and in vivo experiments. The results reveal that GDY–hemin has good biocompatibility and is suitable for wound infection treatment in vivo.
- This article is part of the themed collections: 2021 Materials Chemistry Frontiers HOT articles and Graphyne


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...