Oxidative cross-coupling of thiols for S–X (X = S, N, O, P, and C) bond formation: mechanistic aspects
Abstract
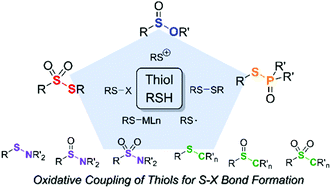
This review focuses on the reactive intermediates (disulfides, sulfenyl halides, thiyl radicals, sulfenium cations, and metal–organosulfur species) and the mechanisms of the recently reported oxidative couplings of thiols. These intermediates are generated by chemical oxidants, transition metal catalysts, electrochemistry, and photochemistry. Chemical oxidant-mediated reactions involve radical, halogenated, or cationic intermediates, or disulfides. Transition metal-catalyzed mechanisms proposed various metal–organosulfur intermediates to elucidate the reactivity and selectivity of metal catalysts. In electro- and photooxidation, direct oxidation/reduction mechanisms of reactants at the electrode or indirect oxidation/reduction of reactants in the presence of redox catalysts have been reported. The following sections are based on the products, thiosulfonates (S–S bond), sulfenamides, sulfinamides, and sulfonamides (S–N bond), sulfinates (S–O bond), thiophosphine oxides and thiophosphates (S–P bond), and sulfides, sulfoxides, and sulfones (S–C bond) and discuss the reaction mechanisms and the above-mentioned key intermediates for product formation. The contents of this review will provide helpful information, guiding the choice of oxidative coupling conditions for the synthesis of various organosulfur compounds with high yields and selectivity.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Synthetic methodology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...