Cryptic halogenation reactions in natural product biosynthesis
Abstract
Covering: Up to December 2020
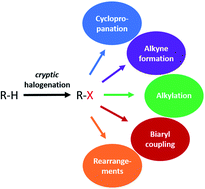
Enzymatic halogenation reactions are essential for the production of thousands of halogenated natural products. However, in recent years, scientists discovered several halogenases that transiently incorporate halogen atoms in intermediate biosynthetic molecules to activate them for further chemical reactions such as cyclopropanation, terminal alkyne formation, C-/O-alkylation, biaryl coupling, and C–C rearrangements. In each case, the halogen atom is lost in the course of biosynthesis to the final product and is hence termed “cryptic”. In this review, we provide an overview of our current knowledge of cryptic halogenation reactions in natural product biosynthesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
