Identification of LASSBio-1945 as an inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (MPRO) through in silico screening supported by molecular docking and a fragment-based pharmacophore model†
Abstract
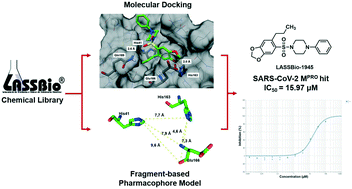
In December 2019, an infectious disease was detected in Wuhan, China, caused by a new pathogenic coronavirus, named SARS-CoV-2. It spread very rapidly, and on March 11th of 2020, the outbreak was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization. Currently, effective treatment options remain limited. SARS-CoV-2 enzyme main protease (MPRO) plays a pivotal role in the viral life cycle, making it a putative drug target. In order to identify suitable hits to develop inhibitors with adequate antiviral properties, we explored the LASSBio Chemical Library employing multiple strategies of virtual screening. A fragment-based pharmacophore model enabled the identification of key interactions involved in the molecular recognition at the catalytic site of MPRO, namely, with amino acid residues His41, His163 and Glu166. Docking-based virtual screening was performed, leading to the identification of LASSBio-1945 (9), a new hit of MPRO, presenting an IC50 = 15.97 μM. This compound, an 1,3-benzodioxolyl sulfonamide, represents an interesting starting point for subsequent hit-to-lead optimization steps and, to the best of our knowledge, a new distinct chemotype for MPRO inhibition.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Coronavirus articles - free to access collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...