Electrospun nanofibers: role of nanofibers in water remediation and effect of experimental variables on their nano topography and application processes
Abstract
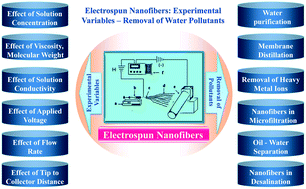
Water is the elixir of life and the most elementary need for the survival of human beings on planet Earth. With rapid industrialization, globalization and human exploitation, natural water resources are diminishing at a startling rate wherein availability of potable water has drastically decreased in recent times and hence membrane technology is a highly pursued area for water purification. The simple and cost-effective electrospinning technique has evolved to be a state-of-the-art method for developing nanofibers of tailored thickness and diameters by combining a broad range of starting materials. This comprehensive review emphasizes on the demonstration of electrospun nanofibers based on their fundamental principles and property–parameter interrelationships as useful filtration membranes. A brief discussion has been provided aiming towards the history of electrospinning, typical apparatus set-up and experimental variables, and latest solutions provided by the scientific community for large scale manufacturing of nanofibers. Further, a detailed overview of the design, fabrication, controlled morphologies, surface functionalization and physicochemical properties of the electrospun nanofibers followed by their useful contributions in the form of filtration membranes and sorbents for water remediation processes such as microfiltration, desalination, heavy metal ion removal, dye removal and oil–water separation has been discussed in detail.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...