Ultraviolet-induced photodegradation elevated the toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics on human lung epithelial A549 cells†
Abstract
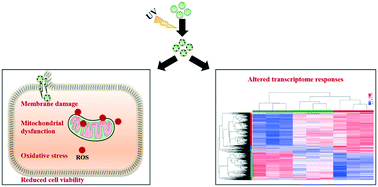
The widespread presence of nanoplastics (NPs), with small particle sizes and high specific surface area, leads to the exposure and potential health risk for humans. The plastic particles widely detected in the indoor and outdoor air imply potential threats to the human respiratory system. However, the impact of aging NPs on their toxicity has been poorly considered, although it is an inevitable process suffered by them once they enter the environment. In this study, the aging of polystyrene (PS) NPs by photodegradation under ultraviolet irradiation for 2 months was investigated, and the toxicities of pristine and aged NPs to human lung epithelial A549 cells were compared. The results revealed alterations in the physicochemical properties with the size of NPs reduced and the abundant oxygen-containing groups formed on the surface. The toxic effects of the pristine and aged NPs at the cellular level on the cell viability, oxidative stress, membrane damage and mitochondrial dysfunction were illustrated in A549 cells, indicating that the aged NPs exhibited greater cytotoxicity than pristine NPs and this toxicity was in a positively aging time-related manner. Transcriptome analysis further revealed the impacts of aged NPs on A549 cells at the molecular level, wherein the aged NPs presented aggravated interference in gene expression, reconfirming the elevated toxicity of NPs after ultraviolet-induced photodegradation. This study highlights the importance of photodegradation on the toxicity of NPs in human health, which is of great significance for the risk assessment of NPs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanomaterials in air


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...