Molecular basis of cerium oxide nanoparticle enhancement of rice salt tolerance and yield†
Abstract
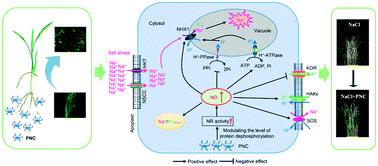
Herein, we demonstrate and elucidate how biocompatible poly(acrylic acid) coated cerium oxide nanoparticles (PNC) improve rice tolerance and crop yield under salinity stress. Rice seedlings hydroponically supplied with PNC (1 μM, 98 μg L−1) have a higher shoot length (33.3%), fresh weight (56.9%), and chlorophyll content (123.9%) compared to controls after being exposed to 100 mM NaCl for 8 days. Similarly, greenhouse experiments reveal that during the reproductive stage, PNC (10 μM, 0.98 mg L−1)-exposed rice plants upon exposure to NaCl stress (7.2 dS m−1; two months) exhibited increased chlorophyll content (23.9%), dry weight (50.5%), and grain weight (47.1%) compared with non-nanoparticle stressed controls. Importantly, the cerium (Ce) content in harvested grains of PNC-supplemented rice plants (18.3 ± 3.1 μg per kg dry weight) is similar to those of samples without nanoparticles, under both control and stress conditions. Molecular evidence showed that PNC enhance nitric oxide (NO) production (30.5%) by inducing the transcription of nia2 (a gene encoding nitrate reductase) and controlling the dephosphorylation of its protein, thus resulting in NO production and plant tolerance against salinity. The crucial role of NIA2-dependent NO synthesis was evaluated by manipulation of endogenous NO levels and in nia2 mutants. The nanoparticle-mediated NO control of salinity tolerance could be explained by reducing reactive oxygen species accumulation (39.5%) and maintaining ion homeostasis. Overall, NO signaling is involved in PNC control of salt tolerance. Our results also indicated that PNC are promising nanobiotechnology tools for improving crop performance and yield in salt stressed fields without increasing the Ce content in cereal grains.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nano-bio interactions


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
