Carbon nanotubes influence the toxic effects of chloramphenicol and tetracycline on cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. in different ways†
Abstract
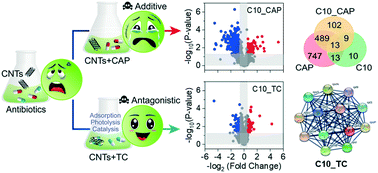
Despite many studies on the toxicity of nanomaterials or antibiotics to aquatic organisms, the combined toxicity of nanomaterials and antibiotics remains poorly understood. This study investigated the joint toxicity of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with chloramphenicol (CAP) or tetracycline (TC) to cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. Both reactive oxygen species (ROS) quenching experiments and proteomic analysis demonstrated that the oxidative stress caused by ROS contributed to the toxicity of CNTs but was irrelevant to the toxicity of CAP and TC despite the increased ROS levels in their exposure groups. CNTs upregulated photosynthesis significantly in response to its oxidative stress and shading effects. CAP vastly inhibited protein biosynthesis and resulted in the small size of cells. TC significantly downregulated the proteins related to periplasmic space which is responsible for cell wall biosynthesis, thereby inducing severe destruction of the cell wall. CNTs mitigated the inhibition effect of CAP on protein biosynthesis, while CAP enhanced the upregulation of proteins induced by CNTs. Consequently, an additive effect was observed between CNTs and CAP according to mortality. In contrast, CNTs exhibited an antagonistic effect with TC due to the strong adsorption and catalytic degradation of TC by CNTs. Moreover, TC can potentiate the CNT-induced downregulation of proteins related to ribosome. This study provides a more realistic insight into the molecular mechanisms of pollutant toxicity and highlights the importance of considering the different combined toxicity of multiple pollutants in the aquatic environment.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Science: Nano Recent HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...