Dynamic aqueous transformations of lithium cobalt oxide nanoparticle induce distinct oxidative stress responses of B. subtilis†
Abstract
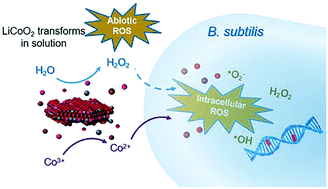
Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), an example of nanoscale transition metal oxide and a widely commercialized cathode material in lithium ion batteries, has been shown to induce oxidative stress and generate intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) in model organisms. In this study, we aimed to understand the time-dependent roles of abiotic ROS generation and Co ions released in aqueous medium by LiCoO2 NPs, and examined the induced biological responses in model bacterium, B. subtilis upon exposure. We found that the redox-active LiCoO2 NPs produced abiotic ROS primarily through H2O2 generation when freshly suspended. Subsequently, the freshly-suspended LiCoO2 NPs induced additional DNA breakage, and changes in expression of oxidative stress genes in B. subtilis that could not be accounted for by the released Co ions alone. Notably, in 48 hour old LiCoO2 suspensions, H2O2 generation subsided while higher concentrations of Co ions were released. The biological responses in DNA damage and gene expression to the aged LiCoO2 NPs recapitulated those induced by the released Co ions. Our results demonstrated oxidative stress mechanisms for bacteria exposed to LiCoO2 NPs were mediated by the generation of distinct biotic and abiotic ROS species, which depended on the aqueous transformation state of the NPs. This study revealed the interdependent and dynamic nature of NP transformation and their biological consequences where the state of NPs resulted in distinct NP-specific mechanisms of oxidative injury. Our work highlights the need to capture the dynamic transformation of NPs that may activate the multiple routes of oxidative stress responses in cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
