AOPs enhance the migration of polystyrene nanoparticles in saturated quartz sand†
Abstract
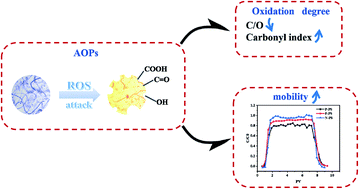
Wastewater treatment plants are suspected to be significant point sources of microplastic and nanoplastic particles (NPs) in the environment. As one of the main wastewater treatment processes, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) may change the physicochemical properties of NPs and further affect their migration. However, limited information is known about the environmental fate of NPs after AOP treatment. In this study, polystyrene nanoparticles were treated using two representative AOPs, Fenton and persulfate treatments, and the migration of the NPs in quartz sand was investigated via column transport experiments. FTIR and XPS analysis indicated that a large number of oxygen-containing groups were generated on the NP surface after AOP treatment leading to lower hydrophobicity and a higher negative charge. Besides, the C/O ratio after Fenton and persulfate treatments was increased from 10.98 to 7.25 and 8.68. Moreover, the NPs after AOP treatment exhibited higher mobility in quartz sand in both ultrapure water and 10 mM NaCl solution. It was more obvious in 10 mM NaCl solution with breakthrough percentages of 79.73% for P-PS, 90.97% for F-PS and 95.67% for N-PS, respectively. These results could be explained by the roles of generated oxygen-containing functional groups; first, the higher negative charge enhanced the electrostatic repulsion between treated NPs and sand; second, lower hydrophobicity improved the binding with water molecules in background solution. This work is helpful in understanding the changes of nanoplastics in AOP treatment and their migration in the natural environment, which has far-reaching influence on the environmental fate and behavior of nanoplastics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Contaminant remediation and fate


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...