Chemosensing of neurotransmitters with selectivity and naked eye detection of l-DOPA based on fluorescent Zn(ii)-terpyridine bearing boronic acid complexes†
Abstract
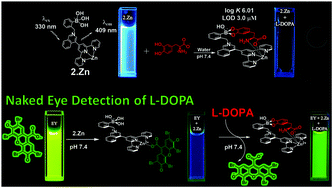
Biological catecholamines such as L-DOPA and dopamine play vital physiological roles in the brain and are chemical indicators of human diseases. A new range of fluorescent Zn(II)-terpyridine complexes are described and studied in-depth as chemosensors for catecholamine-based neurotransmitters and nucleosides in pure water. The new Zn-terpyridine-based chemosensors contain a cationic N-isoquinolinium nucleus as the optical indicator covalently linked to three different isomers of strongly acidified phenylboronic acids (ortho-, 2.Zn; meta-, 3.Zn and para-, 4.Zn, substituted derivatives) as catechol binding sites. The addition of L-DOPA, dopamine, epinephrine, L-tyrosine and nucleosides to Zn(II)-boronic acid chemosensors at physiological pH quenches their blue emission with a pronounced selectivity and an unprecedented high affinity towards L-DOPA (log K = 6.01). This efficient response by L-DOPA was also observed in the presence of coexisting species in blood plasma and urine with a detection limit of 3.0 μmol L−1. A photoinduced electron transfer quenching mechanism with simultaneous chemosensor–L-DOPA complexation in both the excited and ground states is proposed. The fluorescence experimental observations show that the 2.Zn·eosin-Y adduct can be used as a selective naked-eye chemosensing ensemble for L-DOPA with a fast turn-on fluorescent response and color change from blue to green under UV light at the micromolar level. On the basis of multiple spectroscopic techniques (1H, 11B NMR, UV-Vis, and fluorescence), MS-ESI experiments, crystal structures, and DFT calculations, the binding mode between Zn(II)-chemosensors and L-DOPA is proposed in a 1 : 1 model through a cooperative two-point recognition involving the reversible esterification of the boronic acid moiety with the aromatic diol fragment of L-DOPA together with the coordination of the carboxylate anion to the Zn(II) atom with strong electrostatic contribution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...