First-principles calculations of phonon behaviors in graphether: a comparative study with graphene†
Abstract
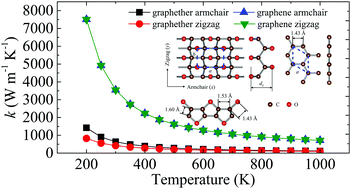
Recently, a two-dimensional (2D) oxocarbon monolayer, graphether, has been arousing extensive attention owing to its excellent electrical properties. In this work, we calculate the lattice thermal conductivity (k) of graphether and graphene using first-principles calculations and the phonon Boltzmann transport equation. At 300 K, the lattice thermal conductivities of graphether and graphene along the armchair direction are 600.91 W m−1 K−1 and 3544.41 W m−1 K−1, respectively. Moreover, the electron localization function is employed to reveal the origin of the anisotropic k of graphether. Furthermore, the harmonic and anharmonic properties of graphether and graphene are analyzed. We attribute the lower k of graphether to the smaller phonon group velocity and shorter phonon lifetime. Finally, the size effects of phonon transport in graphether and graphene are studied, and the results show that the lattice thermal conductivities are significantly dependent on the system length. The analysis of phonon behaviors in our study contributes to an in-depth understanding of the thermal transport in graphether for the first time, which provides valuable guidelines for graphether-based phonon engineering applications and 2D nanoelectronic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...