Spontaneous magnetic merons in a half-metallic Mn2I3Br3 monolayer with easy-plane anisotropy†
Abstract
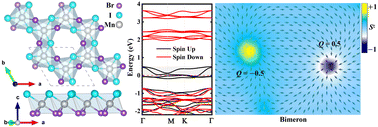
In recent years, great effort has been made in the study of two-dimensional (2D) van der Waals ferromagnets that can stabilize peculiar chiral spin textures, such as magnetic skyrmions and merons. Here, by first-principles calculations and micromagnetic simulations, we systematically investigate the in-plane magnetic anisotropy, Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction (DMI) and magnetic merons in a Mn2I3Br3 monolayer. Mn2I3Br3 exhibits half-metallic behavior with a large band gap (∼2.7 eV) for spin-down electrons, but is gapless for spin-up ones. In addition, unlike most 2D ferromagnets with an off-plane magnetic easy axis and negligible DMI, the magnetic easy axis of Mn2I3Br3 is in-plane, with a large magnetic anisotropy energy of −13.2 meV and a strong DMI of 4.6 meV, which are mainly induced by the strong spin–orbital coupling of I atoms, microscopically. In particular, spontaneous magnetic merons, stabilized by the DMI, can exist in a wide magnetic field range (0–6 T). Our work not only provides important guidelines for the investigation of the DMI and merons in half-metallic materials, but also demonstrates the Mn2I3Br3 monolayer as an ideal platform to explore the deep physics of magnetic merons and as a promising candidate for magnetic storage devices, as well as spin filters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...