Highly crystalline sodium manganese ferrocyanide microcubes for advanced sodium ion battery cathodes†
Abstract
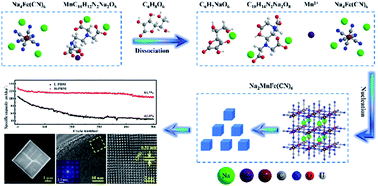
The microstructure and morphology of the crystal play an important role in the physical and electrochemical properties of electrode materials. Here we report a highly crystalline microcube structure of Na-rich Prussian white Na1.92Mn[Fe(CN)6]0.98 for sodium ion battery cathodes. The obtained structure features high crystallinity of the monoclinic structure with an average cubic size of 3–5 μm. Because of the improvement on microstructural and electrical properties, the cathode design enables promising electrochemical performance. The electrode exhibits an outstanding rate performance with reversible capacities of 152.8 mA h g−1 (10 mA g−1), 128.1 mA h g−1 (100 mA g−1), 118.7 mA h g−1 (500 mA g−1) and 110.3 mA h g−1 (1000 mA g−1). It also exhibits a good cycling performance with a capacity retention of 82% after 500 cycles at 100 mA g−1. More importantly, the XRD analysis reveals a highly reversible monoclinic–cubic–monoclinic structural evolution of the cathode upon Na+ extraction/insertion. The good rate and cycling performance can be attributed to the robust crystal structure with few defects and fast Na+ transfer kinetics. The high purity single crystal morphology can also reduce the side reactions on the electrode/electrolyte interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...