Unexpected hydrophobicity on self-assembled monolayers terminated with two hydrophilic hydroxyl groups†
Abstract
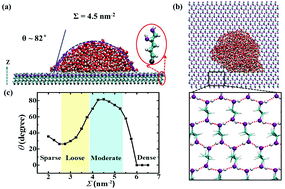
Current major approaches to access surface hydrophobicity include directly introducing hydrophobic nonpolar groups/molecules onto the surface or elaborately fabricating surface roughness. Here, for the first time, molecular dynamics simulations show an unexpected hydrophobicity with a contact angle of 82° on a flexible self-assembled monolayer terminated only with two hydrophilic OH groups ((OH)2-SAM). This hydrophobicity, verified by a water slip phenomenon characterizing the friction on the (OH)2-SAM surface, is attributed to the formation of a hexagonal-ice-like H-bonding structure in the OH matrix of (OH)2-SAM, which sharply reduces the hydrogen bonds between the surface and the water molecules above. The unique simple interface presented here offers a significant molecular-level platform for examining the bio-interfacial interactions ranging from biomolecule binding to cell adhesion.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...