Mechanistic insights into the inhibition and size effects of graphene oxide nanosheets on the aggregation of an amyloid-β peptide fragment†
Abstract
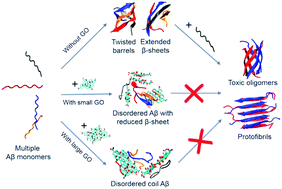
The aggregation of amyloid-β (Aβ), which involves the formation of small oligomers and mature fibrils, has received considerable attention in the past few decades due to its close link with Alzheimer's disease (AD). The inhibition of β-sheet formation has been considered as the primary therapeutic strategy for AD. In this respect, graphene oxide (GO) has gained significant attention because of its high solubility, good biocompatibility and inhibitory effect on the aggregation of Aβ and the 33–42 fragment (Aβ33–42). However, the inhibitory mechanism at the atomic level remains elusive. Herein, we investigated the oligomerization of Aβ33–42 by performing replica exchange molecular dynamics simulations on four Aβ33–42 peptide chains in the absence and presence of two different sizes of GO. Our simulations show that isolated Aβ33–42 can form fibril-prone extended β-sheets and barrel-like structures, whereas they are suppressed in the presence of GO nanosheets. Our data reveal that GO inhibits Aβ33–42 oligomerization by making Aβ33–42 peptides separate from each other through strong interactions with M35. With the same total number of atoms, GO120 displays better inhibitory effect than GO60 by providing a larger effective contact surface area. This study provides the molecular mechanism of GO in inhibiting the aggregation of Aβ33–42, which might offer a theoretical insight into the design of drugs against AD at the atomic level.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...