Aggregation effects on photophysical properties of NBN-doped polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a theoretical study†
Abstract
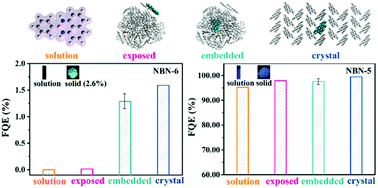
To realize the precise manipulation of the optoelectrical properties of boron–nitrogen (B–N) unit-doped polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), unraveling the structure–property relationship behind them is of vital importance. In this work, we take two representative NBN-doped PAHs with similar structures (NBN-5 and NBN-6) as examples and explore the influence of molecular packing on their photophysical properties in different environments (including dilute solution, amorphous aggregate and crystal) using a theoretical protocol that combines molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and thermal vibration correlation function coupled quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) calculations. We found that the different symmetries of the transition orbitals in NBN-5 and NBN-6 lead to their distinct distributions of transition orbitals, with NBN-5 delocalizing on the whole backbone and NBN-6 bearing clear intramolecular charge transfer. Therefore, the S1 state of NBN-6 demonstrates redshifted emission spectra in contrast to those of NBN-5. We confirmed that NBN-6 in dilute solution is more flexible than NBN-6 in aggregated states. After aggregation, the fluorescent quantum efficiency (FQE) of NBN-6 increases significantly with the nonradiative decay constants decreasing by 2–4 orders of magnitude, because the dense molecular packing in the aggregated state could effectively suppress the out-of-plane rotation and distortion of the phenyl-ring at the boron position, indicating its AIE feature. While the photophysical properties of conjugated NBN-5 with high rigidity are independent of the environment, showing bright emission in both solution and solid states, consistent with the experimental results. Our theoretical protocol is general and applicable to other doped PAHs, thus laying a solid foundation for the rational design of advanced materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...