Detection and identification of human fungal pathogens using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and principal component analysis†
Abstract
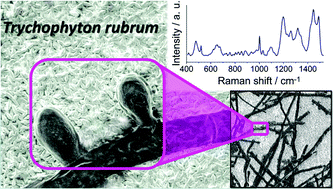
This paper demonstrates that surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) coupled with principal component analysis (PCA) can serve as a fast and reliable technique for the detection and identification of human fungal pathogens, such as Trichophyton rubrum, Candida krusei, Scopulariopsis brumptii, and Aspergillus flavus. Fungal infections have become one of the leading infectious causes of morbidity and mortality among hospitalized patients and/or immunocompromised hosts. Hence, there is a strong need for the development of new technologies allowing for fast and reliable diagnosis of fungal diseases. Our study shows that the SERS technique effectively distinguishes between selected common fungal pathogens and thus offers taxonomic affiliation of fungi within several minutes. Additionally, the PCA analysis allows performing statistical classification of fungal pathogens studied and identifying the fungal spectrum directly from a clinical sample. Calculated two principal components (PCs) (PC-1, PC-2) are the most diagnostically significant, explain 97% of the variability and enable, with very high probability, discrimination between the four mentioned fungal species. Moreover, the results of this study demonstrate the excellent possibility for the identification of fungi from human skin samples. The research presented in this paper offers an alternative for conventional fungal diagnostics and paves the way for the development of a new, fast, robust, and cost-effective diagnostic test for the detection and identification of fungal pathogens.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...