Morphology and properties of PEDOT:PSS/soft polymer blends through hydrogen bonding interaction and their pressure sensor application†
Abstract
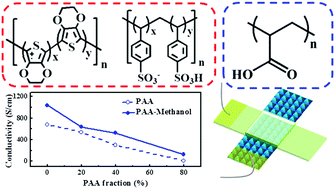
We report the effects of the composition on the stretchability and conductivity of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) polymer blends with soft polymers including poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), poly(acrylic acid) (PAA), and poly(methacrylic acid) (PMAA) and their application in pressure sensors. The composition–stretchability relationship was investigated with the stress–strain curves of the bulk films. Among these polymer blends, PAA-based blends outperformed in stretchability, attributed to the low glass transition temperature and ductile nature of PAA. And the composition–conductivity relationship was studied with conductive atomic force microscopy, Gaussian simulation and infrared spectroscopy. The PAA-based blends presented well-dispersed morphology for PEDOT and the strongest hydrogen bonding network between PAA and PEDOT:PSS was created through the blending, which gave rise to stable and high conductivity. Furthermore, the conductivity of the PEDOT:PSS/PAA blend at 20/80 wt ratio was largely increased (13 to 125 S cm−1) and stretchability (elongation at break) increased from 20 to 40% through methanol treatment. Finally, PAA-based blends treated with methanol were applied to the pressure sensor device, achieving a very high sensitivity of 39.90 kPa−1 at 20% tensile strain, a quick response time of around 49 ms, and a low detection limit of about 27.4 Pa. This study suggested a novel and facile approach to manipulate the structure and stretchability of the PEDOT:PSS polymer blending system for stretchable electronics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry C Lunar New Year collection 2021


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...