Tuning hydrogel properties with sequence-defined, non-natural peptoid crosslinkers†
Abstract
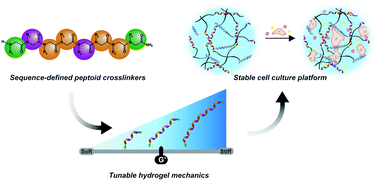
The native extracellular matrix (ECM) is composed of hierarchically structured biopolymers containing precise monomer sequences and chain shapes to yield bioactivity. Recapitulating this structure in synthetic hydrogels is of particular interest for tissue engineering and in vitro disease models to accurately mimic biological microenvironments. However, despite extensive research on hydrogels, it remains a challenge to recapitulate the hierarchical structure of native ECM with completely synthetic hydrogel platforms. Toward this end, this work presents a synthetic hydrogel system using commercially available poly(ethylene glycol) macromers with sequence-defined poly(N-substituted glycines) (peptoids) as crosslinkers. We demonstrate that bulk hydrogel mechanics, specifically as shear storage modulus, can be controlled by altering peptoid sequence and structure. Notably, the helical peptoid sequence investigated here increases the storage modulus of the resulting hydrogels with increasing helical content and chain length, in a fashion similar to helical peptide-crosslinked hydrogels. In addition, the resulting hydrogels are shown to be hydrolytically and enzymatically stable due to the N-substituted peptidomimetic backbone of the crosslinkers. We further demonstrate the potential utility of these peptoid-crosslinked hydrogels as a viable cell culture platform using seeded human dermal fibroblasts in comparison to peptide-crosslinked hydrogels as a control. Taken together, our system offers a strategy toward ECM mimics that replicate the hierarchy of biological matrices with completely synthetic, sequence-defined molecules.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry B Emerging Investigators


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...