Extended linear detection range of a Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 thin film-based self-powered UV photodetector via current and voltage dual indicators†
Abstract
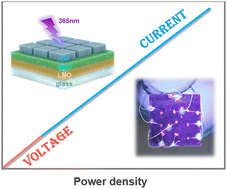
Ferroelectric materials are widely recognized for their ability to generate photovoltaic voltages larger than their bandgap, making them ideal candidates for photodetector applications. Here, we report a self-powered UV photodetector based on a Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 (BNT) thin film prepared by the sol–gel method. Compared with conventional photodetectors based on a single detection indicator, the demonstrated photodetector realizes UV light intensity detection over a wide linear range using a current and voltage dual indicator detection method. When the UV light intensity is lower than 1.8 mW cm−2, the voltage can be used to detect the light signal. Conversely, the current can be utilized to detect the signal. This method not only broadens the linear detection range of UV light intensity, making it possible to detect weak UV light of 45.2 nW cm−2, but also allows the detector to maintain relatively high sensitivity within the detectable range. To investigate the distribution of spatial UV light intensity, a self-powered photodetector array system has been utilized to record the output voltage signals as a map.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...