Printed carbon nanotube thin-film transistors: progress on printable materials and the path to applications
Abstract
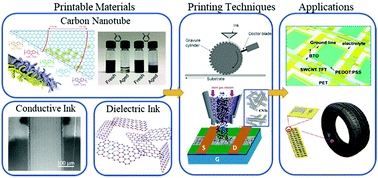
Printing technologies have attracted significant attention owing to their potential use in the low-cost manufacturing of custom or large-area flexible electronics. Among the many printable electronic materials that have been explored, semiconducting carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have shown increasing promise based on their exceptional electrical and mechanical properties, relative stability in air, and compatibility with several printing techniques to form semiconducting thin films. These attractive attributes make printed CNT thin films promising for applications including, but not limited to, sensors and display backplanes – at the heart of which is electronics’ most versatile device: the transistor. In this review, we present a summary of recent advancements in the field of printed carbon nanotube thin-film transistors (CNT-TFTs). In addition to an introduction of different printing techniques, together with their strengths and limitations, we discuss key aspects of ink/material selection and processing of various device components, including the CNT channels, contacts, and gate insulators. It is clear that printed CNT-TFTs are rapidly advancing, but there remain challenges, which are discussed along with current techniques to resolve them and future developments towards practical applications from these devices. There has been interest in low-cost, printable transistors for many years and the CNT-TFTs show great promise for delivering, but will not become a reality without further research advancement.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...