Protein unfolding by SDS: the microscopic mechanisms and the properties of the SDS-protein assembly†
Abstract
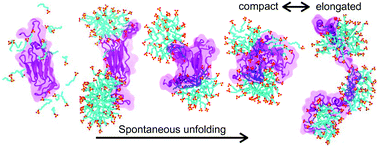
The effects of detergent sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) on protein structure and dynamics are fundamental to the most common laboratory technique used to separate proteins and determine their molecular weights: polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. However, the mechanism by which SDS induces protein unfolding and the microstructure of protein–SDS complexes remain largely unknown. Here, we report a detailed account of SDS-induced unfolding of two proteins—I27 domain of titin and β-amylase—obtained through all-atom molecular dynamics simulations. Both proteins were found to spontaneously unfold in the presence of SDS at boiling water temperature on the time scale of several microseconds. The protein unfolding was found to occur via two distinct mechanisms in which specific interactions of individual SDS molecules disrupt the protein's secondary structure. In the final state of the unfolding process, the proteins are found to wrap around SDS micelles in a fluid necklace-and-beads configuration, where the number and location of bound micelles changes dynamically. The global conformation of the protein was found to correlate with the number of SDS micelles bound to it, whereas the number of SDS molecules directly bound to the protein was found to define the relaxation time scale of the unfolded protein. Our microscopic characterization of SDS–protein interactions sets the stage for future refinement of SDS–enabled protein characterization methods, including protein fingerprinting and sequencing using a solid-state nanopore.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Theoretical Modelling at Nano-bio Interfaces


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
