Photoinduced synthesis of Bi2O3 nanotubes based on oriented attachment†
Abstract
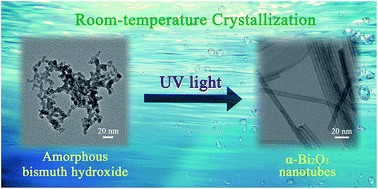
Photoinduced synthesis of inorganic nanomaterials has attracted great attention recently. Herein, we demonstrate the facile photoinduced synthesis of Bi2O3 nanotubes with a uniform pore size of about 2.2 nm at room temperature. Ultraviolet irradiation promoted the crystallization of amorphous bismuth hydroxide into bismuth oxide. The formation of this special tubular morphology of α-Bi2O3 was attributed to the small size of the bismuth hydroxide precursor and oriented attachment mechanism. What's more, α-Bi2O3 nanotubes can further convert to Bi2O2CO3 nanosheets in organic solution with ultraviolet irradiation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...