TiO2 exposure alters transition metal ion quota in Rhodococcus ruber GIN-1†
Abstract
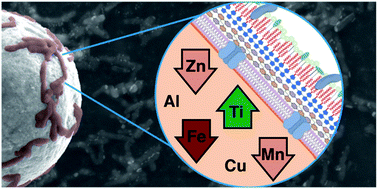
After exposure to micron-sized TiO2 particles, anatase and/or rutile, Rhodococcus ruber GIN-1 accumulates an increased concentration (2.2 ± 0.2 mg kg−1) of mobilized Ti into its biomass with concomitant decreases in cellular biometals Fe, Zn, and possibly Mn, while levels of Cu and Al are unaffected.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...