Natural cordycepin induces apoptosis and suppresses metastasis in breast cancer cells by inhibiting the Hedgehog pathway†
Abstract
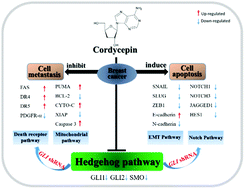
In the study, we investigated the role of the hedgehog (Hh) pathway in cordycepin's effects on human breast cancer cells, with respect to cell growth, apoptosis and metastasis. We found cordycepin to have low toxicity but significant anticancer effects. Cordycepin-induced apoptosis led to increased PUMA, CYTO-C, FAS, DR4/5, and cleaved caspase-3; and decreased BCL-2, XIAP and PDGFR-α. Cordycepin inhibited metastasis, which was associated with up-regulated E-cadherin, and down-regulated N-cadherin, SNAIL, SLUG and ZEB1. Cordycepin also inhibited expression of Hh pathway components and GLI transcriptional activity. Inversely, knockout of GLI blocked cordycepin-mediated effects on the apoptotic, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and Notch pathways, which indicates that GLI is crucial for cordycepin's effects against breast cancer. Inhibition of GLI enhanced cordycepin's effect on breast cancer cell growth. To our knowledge, this is the first study of cordycepin's effect on the Hh pathway in breast cancer, and provides preliminary data for the in vivo study, and possible therapeutic use, of cordycepin.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...