Effect of high energy electron beam on proteolysis and antioxidant activity of rice proteins
Abstract
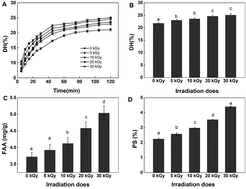
This research focused on the effects of electron beam irradiation (EBI) on the hydrolysis and antioxidant activity of rice proteins (RPs). The RPs were treated with 0, 5, 10, 20 and 30 kGy doses of EBI. The results showed that EBI pretreatment improved significantly (P < 0.05) the degree of hydrolysis, increasing the DH value by more than 15.09% at a dose of 30 kGy. In addition, radical scavenging results showed that EBI treatment had effects on antioxidant activity and could increase the DPPH and ABTS+ radical scavenging activity of rice protein hydrolysates (RPHs) by 32.06% and 79.11%, respectively (30 kGy). The CAA test also confirmed that EBI pretreatment could effectively improve the ability of RPHs to remove intracellular free radicals. Scanning electron microscopy indicated that EBI treatment destroyed microstructures and resulted in cracks and fragments of RPs. Circular dichroism analysis showed that EBI affected the secondary structure of RPs by destroying the α-helix structure. Changes in the UV visible spectra indicated unfolding of RPs by EBI. Amino acid and molecular weight distribution analysis revealed that EBI pretreatment could increase the ratio of antioxidant-related amino acids and produce smaller peptides. Therefore, EBI pretreatment is an efficient method to promote protein proteolysis due to its effect on the molecular conformation as well as on protein microstructure. Moreover, EBI treatment applied before enzymatic hydrolysis has the potential to prepare hydrolysates with high bioactivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...