Rapid characterization of arsenic adsorption on single magnetite nanoparticles by collisions at microelectrodes†‡
Abstract
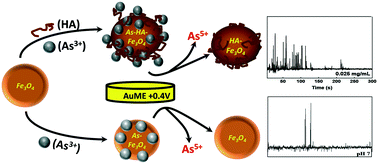
We describe a rapid and sensitive electrochemical approach to evaluate the interaction of arsenite (As3+) with magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles (MNPs) by single particle collision electrochemistry (SPCE). The method is based on direct measurements of the (As3+) adsorbed on single MNPs, quantified via the oxidation of As3+ to As5+ at 0.4 V vs. Ag/AgCl, as the As-MNPs collide with a gold microelectrode (AuME). Measurement of the intensity of current spikes and the charge passed per impact spike provides a measure of As3+ content adsorbed per MNP. The total calculated charge passed at AuME was monitored over 400 s collision time and the As3+ adsorption was quantified at different pH and environmental conditions. The charge increased significantly for MNPs exposed to a natural organic material, humic acid (HA), at concentrations of up to 5 ppm, and when the pH of the solution was between 6 and 8, indicating enhanced adsorption. The concentration of As3+ (0.013–0.036 fM As/MNP) was found to correlate well with the initial concentration of As3+ in solution (0.001–10 μM), suggesting that the method can also be used as an analytical tool to determine As contamination in environmental samples. The results were confirmed with spectroscopic techniques and demonstrate As3+ adsorption. Overall, this study demonstrates the capability of SPCE to fundamentally probe the surface properties of magnetite with high resolution and elemental specificity allowing a direct ultrasensitive assessment of the As3+ loading on individual MNPs. This approach could be used as a simple cost effective and fast screening tool to evaluate heavy metal ion adsorption on nanomaterial sorbents for environmental monitoring and remediation applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Remediation


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
