Responsive fluorinated nanoemulsions for 19F magnetic resonance detection of cellular hypoxia†
Abstract
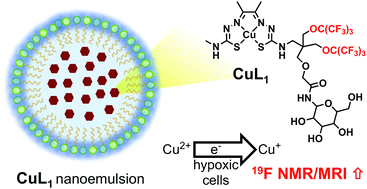
We report two highly fluorinated Cu-based imaging agents, CuL1 and CuL2, for detecting cellular hypoxia as nanoemulsion formulations. Both complexes retained their initial quenched 19F MR signals due to paramagnetic Cu2+; however, both complexes displayed a large signal increase when the complex was reduced. DLS studies showed that the CuL1 nanoemulsion (NECuL1) had a hydrodiameter of approximately 100 nm and that it was stable for four weeks post-preparation. Hypoxic cells incubated with NECuL1 showed that 40% of the Cu2+ taken up was reduced in low oxygen environments.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent: Americas


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
